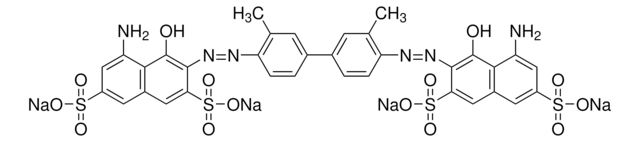
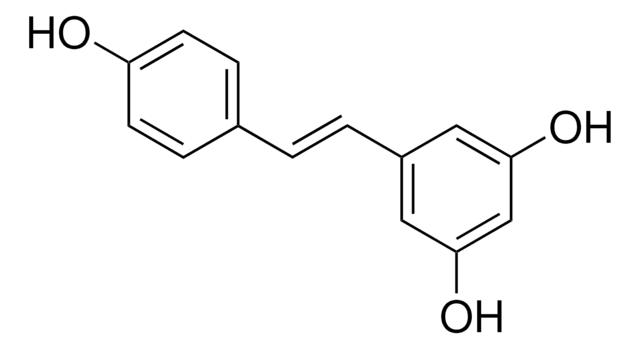
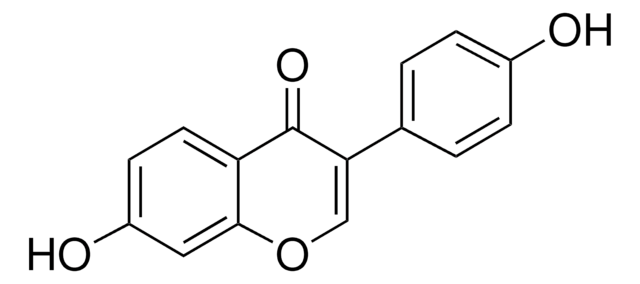
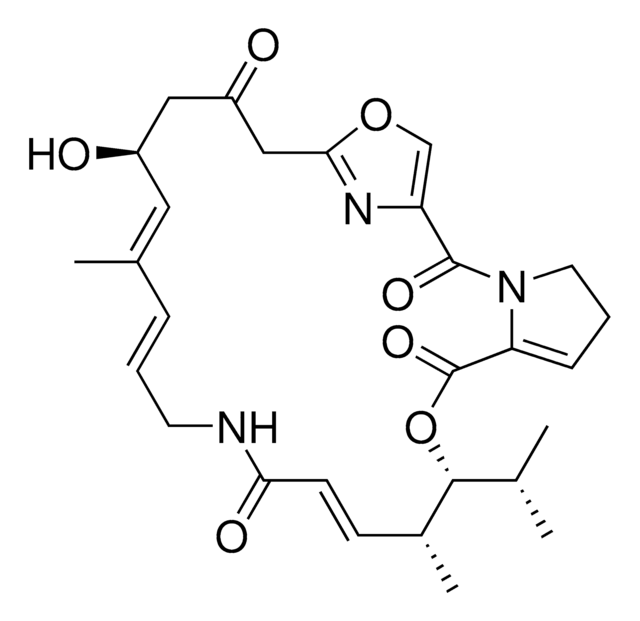
Recommended Products
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
1 of 4
This Item | C0755 | A9275 | C7786 |
|---|---|---|---|
| form powder | form powder | form lyophilized powder | form powder |
| storage temp. −20°C | storage temp. −20°C | storage temp. 2-8°C | storage temp. −20°C |
General description
Application
- as a control protein for immobilization on-chip for deep purple protein staining methods for monitoring post-translation modifications[3]
- as a substrate for casein kinase Iε in in vitro casein kinase assay[4]
- as a standard in gel filtration chromatography (GFC) and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) for quantification of phosvitin from egg extracts[5]
- for immobilization onto Layer-by-Layer (LbL) for Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy-attenuated total reflectance (FTIR-ATR) studies[6]
Biochem/physiol Actions
Other Notes
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Need A Sample COA?
This is a sample Certificate of Analysis (COA) and may not represent a recently manufactured lot of this specific product.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service