A2382
Azoalbumin
protease substrate
Synonym(s):
Sulfanilic acid-azoalbumin
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
bovine
Quality Level
form
powder
concentration
60-90% (Lowry)
technique(s)
tissue culture: suitable
solubility
0.01 M HCl: soluble 25 mg/mL
storage temp.
2-8°C
General description
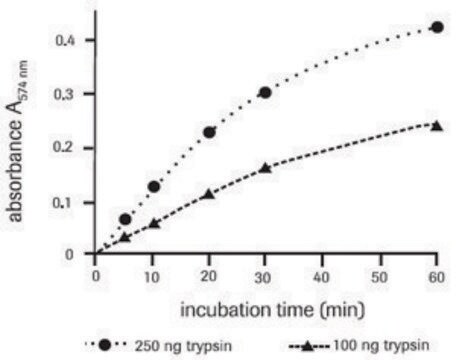
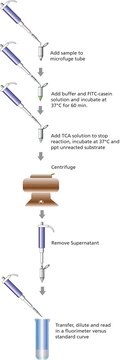
Azoalbumin is a substrate for assaying proteolytic enzymes, majorly trypsin, pepsin and cysteine proteinase. The assay method offers precision and is easy to perform.
Application
Azoalbumin has been used:
- as a substrate for enzymatic assay of hyphal extracts
- for screening general protease activity in spent growth medium extract
- for screening S. rolfsii proteases
Preparation Note
Prepared from Bovine albumin, Fraction V (A 4503)
Substrates
A soluble chromogenic substrate for proteolytic enzymes.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Inhibition of digestive trypsin-like proteases from larvae of several lepidopteran species by the diagnostic cysteine protease inhibitor E-64
Novillo C, et al.
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 27(3), 247-254 (1997)
A modified azoalbumin technique for the assay of proteolytic enzymes for use in blood group serology.
Phillips PK, et al.
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 37(3), 329-331 (1984)
Feces derived allergens of Tyrophagus putrescentiae reared on dried dog food and evidence of the strong nutritional interaction between the mite and Bacillus cereus producing protease bacillolysins and exo-chitinases
Erban T, et al.
Frontiers in Physiology, 7(3), 53-53 (2016)
Optimisation of cellobiose dehydrogenase production by the fungus Sclerotium (Athelia) rolfsii
Ludwig R and Haltrich D
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 61(1), 32-39 (2003)
B Cook et al.
Journal of reproduction and fertility, 51(1), 65-71 (1977-09-01)
No unusual steroid-binding proteins that might react with the oocyte or its investments could be detected in follicular fluid. Corticosteroid-binding globulin occurred in follicular fluid from pigs, sheep and cows, and sex hormone-binding globulin occurred in follicular fluid from sheep
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service