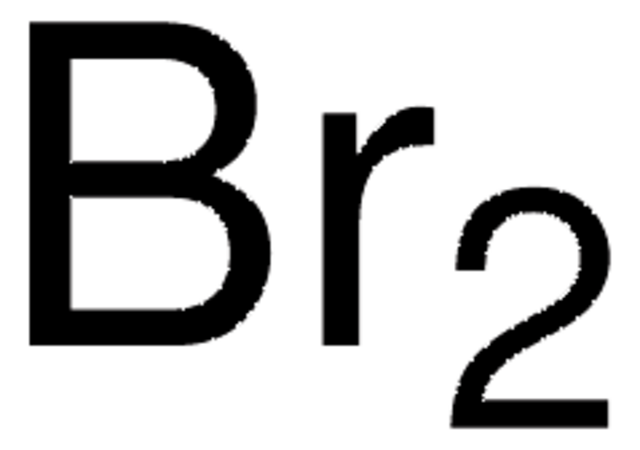About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
ACS reagent
Quality Level
vapor density
7.14 (vs air)
vapor pressure
175 mmHg ( 20 °C)
671 mmHg ( 55 °C)
Assay
≥99.5%
form
liquid
resistivity
7.8E18 μΩ-cm, 20°C
impurities
organic bromine compounds, passes test
≤0.001% I2
≤0.001% S compounds
evapn. residue
≤0.005%
bp
58.8 °C (lit.)
mp
−7.2 °C (lit.)
density
3.119 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
anion traces
chloride (Cl-): ≤0.05%
cation traces
Ni: ≤5 ppm
heavy metals: ≤2 ppm
SMILES string
BrBr
InChI
1S/Br2/c1-2
InChI key
GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- Aromatic and heterocyclic compounds.
- Carbonyl compounds at α position to carbonyl groups.
- Aromatic carboxylic acids via Hell-Volhard-Zelinski reaction in the presence of phosphorus trihalides.
- Alkylbenzenes at the benzylic position using photocatalytic conditions.
It can also be used as an oxidizing agent for the oxidation of:
- Primary alcohols to either aldehydes or esters.
- Secondary alcohols to ketones.
It can also be used as a Lewis acid catalyst to:
- Convert epoxides and CO2 to cyclic carbonates in a continuous flow system.
- Synthesize bis(indolyl)methanes by reacting indoles with carbonyl compounds.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 1 Inhalation - Aquatic Acute 1 - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1A
Storage Class Code
6.1B - Non-combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service