385570
Heat Shock Factor 1 Inhibitor, KRIBB11
The Heat Shock Factor 1 Inhibitor, KRIBB11 controls the biological activity of Heat Shock Factor 1.
Synonym(s):
Heat Shock Factor 1 Inhibitor, KRIBB11, Hsp70 Induction Inhibitor II, N²-(1H-Indazol-5-yl)-N⁶-methyl-3-nitropyridine-2,6-diamine, HSF1 Inhibitor, KRIBB11, Heat Shock Protein Inhibitor III, p-TEFb hsp70 Promoter Recruitment Inhibitor
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥98% (HPLC)
form
solid
manufacturer/tradename
Calbiochem®
storage condition
OK to freeze
protect from light
color
orange-yellow
solubility
DMSO: 50 mg/mL, brown
shipped in
ambient
storage temp.
−20°C
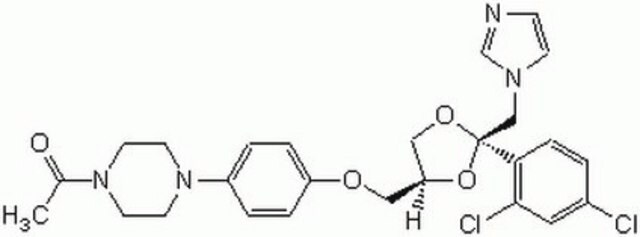
SMILES string
CNC(C=C1)=NC(NC2=CC3=C(NN=C3)C=C2)=C1[N+]([O-])=O
General description
Packaging
Warning
Reconstitution
Other Notes
Legal Information
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service