517933
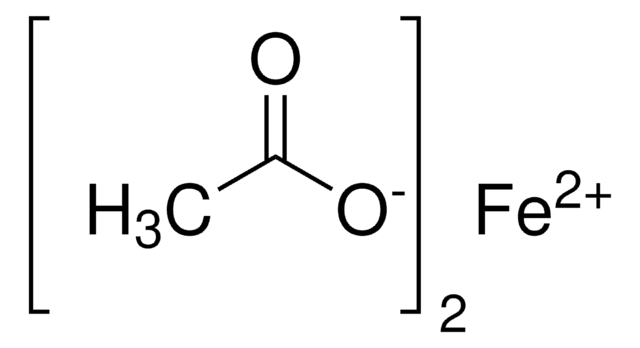
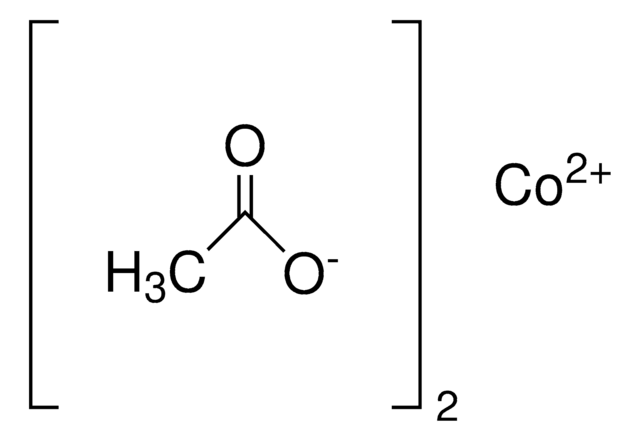
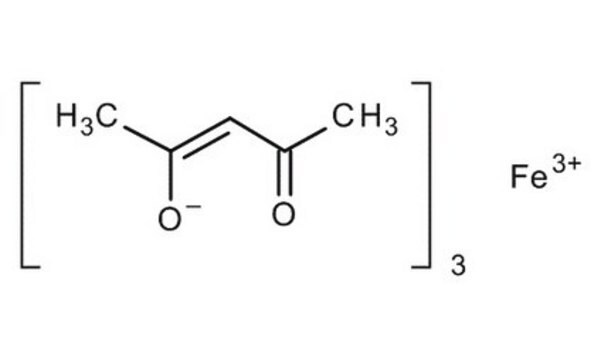
Iron(II) acetate
≥99.99% trace metals basis
Synonym(s):
Ferrous acetate, Iron acetate [Fe(OAc)2 ], Iron diacetate
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥99.99% trace metals basis
form
solid
reaction suitability
core: iron
mp
190-200 °C (dec.) (lit.)
SMILES string
CC(=O)O[Fe]OC(C)=O
InChI
1S/2C2H4O2.Fe/c2*1-2(3)4;/h2*1H3,(H,3,4);/q;;+2/p-2
InChI key
LNOZJRCUHSPCDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-L
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- A precursor for synthesizing iron oxide and iron-based nanostructures which are employed as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries and supercapacitors.
- A precursor in the synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles. These particles are incorporated into carbon nanofibers for use in supercapacitor applications.
- A precursor to synthesize hematite nanoparticles for applications in solar cells. These nanoparticles exhibit shape-dependent optical properties and can be used for imaging, photocatalysis, and solar cells. The product was used to synthesize iron oxide nanoparticles which was further used to form iron oxide-poly(ethylene glycol) core-shell nanoparticles (NPs). The core-shell NPs were studied for self-assembly at liquid–liquid interfaces (SALI) forming monolayers.
Packaging
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Professor Randal Lee (University of Houston, USA) discusses design considerations for iron oxide magnetic nanospheres and nanocubes used for biosensing, including synthetic procedures, size, and shape. The effects of these variables are discussed for various volumetric-based and surface-based detection schemes.
Magnetism and magnetic materials have been of scientific interest for over 1,000 years. More recently, fundamental investigations have focused on exploring the various types of magnetic materials and understanding the magnetic effects created by electric currents.
The properties of many devices are limited by the intrinsic properties of the materials that compose them.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service