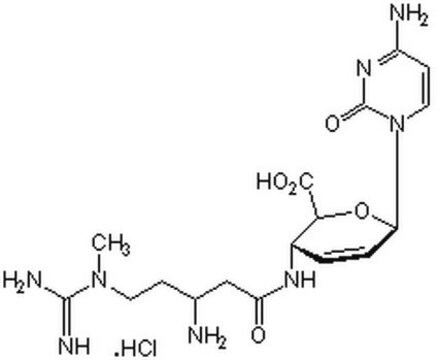
H3274
Hygromycin B from Streptomyces hygroscopicus
powder, non-animal origin, suitable for cell culture and insect cell culture, BioReagent
Synonym(s):
Hygromycin
About This Item
Recommended Products
product name
Hygromycin B from Streptomyces hygroscopicus, powder, BioReagent, suitable for cell culture, suitable for insect cell culture
biological source
Streptomyces hygroscopicus
Quality Level
product line
BioReagent
form
powder
concentration
≥60% (HPLC)
technique(s)
cell culture | insect: suitable
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
color
faintly brown to brown
white to beige
(1) 7.1, (2) 8.8
mp
160-180 °C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Antimicrobial Spectrum: Hygromycin B acts against bacteria, fungi and higher eukaryotic cells.
Caution
Preparation Note
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 1 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 2 Dermal - Acute Tox. 2 Oral
Storage Class Code
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Need A Sample COA?
This is a sample Certificate of Analysis (COA) and may not represent a recently manufactured lot of this specific product.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
Protein synthesis is a complex, multi-step process involving many enzymes as well as conformational alignment. However, the majority of antibiotics that block bacterial protein synthesis interfere with the processes at the 30S subunit or 50S subunit of the 70S bacterial ribosome.
Antibiotic kill curve is a dose response experiment in which mammalian cells are subjected to increasing amounts of selection antibiotic
Protocols
Extraction and quantitative analysis of aminoglycosides in porcine tissue, using molecular imprinted polymer solid phase extraction followed by LC-MS/MS.
Stem Cell protocols for cryopreservation, thawing of cryopreserved stem cells and media preparation.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service