D2629
6-(Dimethylamino)purine
≥98%
Synonym(s):
6-DMAP, N6,N6-Dimethyladenine
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(5)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C7H9N5
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
163.18
Beilstein:
7634
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
41106305
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.51
Recommended Products
biological source
synthetic (organic)
Quality Level
Assay
≥98%
form
powder
mp
259-262 °C (lit.)
solubility
water: 50 mg/mL, clear to hazy, colorless to light yellow
storage temp.
−20°C
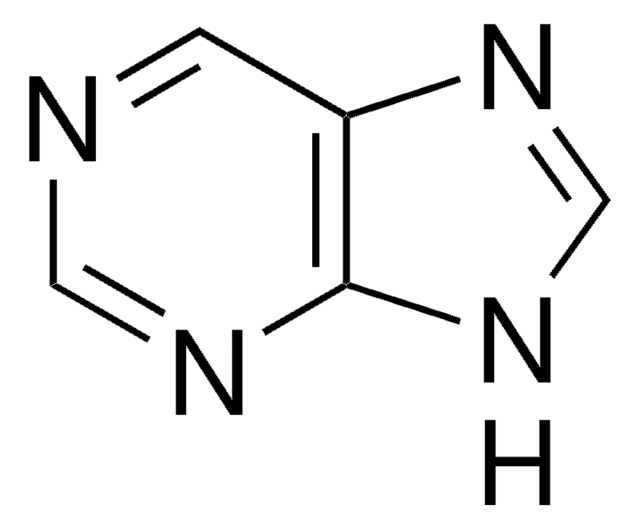
SMILES string
CN(C)c1ncnc2[nH]cnc12
InChI
1S/C7H9N5/c1-12(2)7-5-6(9-3-8-5)10-4-11-7/h3-4H,1-2H3,(H,8,9,10,11)
InChI key
BVIAOQMSVZHOJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
6-(Dimethylamino)purine (6-DMAP) is a purine-based metabolite with two condensed heterocyclic rings and two methyl groups linked to the amino group of the purine unit of adenine.
Application
6-(Dimethylamino)purine has been used:
- as a supplement in GR-1 aa medium (bovine medium) for parthenogenetic activation of bovine oocytes to study its potential for embryo development
- in the activation step during the production of nuclear transfer embryos
- as a supplement in HCR2aa medium to activate interspecies embryos derived from interspecies somatic cell nuclear transfer (iSCNT) technique
Biochem/physiol Actions
6-(Dimethylamino)purine (6-DMAP) is a protein kinase and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor. It acts as a secondary metabolite and mediates RNA modification. 6-DMAP is a potent cytokinetic inhibitor and is used in parthenogenesis and meiosis studies. It is also used to promote pronuclei formation in mammalian oocytes. 6-DMAP is a dual fluorescence molecule according to femtosecond fluorescence up-conversion spectroscopy studies.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Gaid Le Beux et al.
Theriogenology, 60(6), 1049-1058 (2003-08-26)
Improvement of the ability to maintain germinal vesicle stage oocytes in vitro is important for the acquisition of developmental competence. Maintaining oocytes at this stage without damaging their quality would allow synchronization of maturation and homogenization of the oocytes population.
Karen Versieren et al.
Fertility and sterility, 96(3), 624-628 (2011-07-22)
To create a pool of frozen donated human oocytes and find the optimal stage for slow controlled-rate freezing of human in vitro matured oocytes. Oocytes at different developmental stages of maturation (germinal vesicle, metaphase I, or metaphase II) and oocytes that
De Cheng et al.
PloS one, 7(12), e51778-e51778 (2012-12-20)
Porcine induced pluripotent stem (piPS) cell lines have been generated recently by using a cocktail of defined transcription factors, however, the features of authentic piPS cells have not been agreed upon and most of published iPS clones did not meet
Marcin Szpila et al.
Scientific reports, 9(1), 11859-11859 (2019-08-16)
Postovulatory ageing of mammalian oocytes occurs between their ovulation and fertilization and has been shown to decrease their developmental capabilities. Aged oocytes display numerous abnormalities, including altered Ca2+ signalling. Fertilization-induced Ca2+ oscillations are essential for activation of the embryonic development
Justine Collier
Current opinion in microbiology, 12(6), 722-729 (2009-09-29)
N(6)-methyl-adenines can serve as epigenetic signals for interactions between regulatory DNA sequences and regulatory proteins that control cellular functions, such as the initiation of chromosome replication or the expression of specific genes. Several of these genes encode master regulators of
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service