A6508
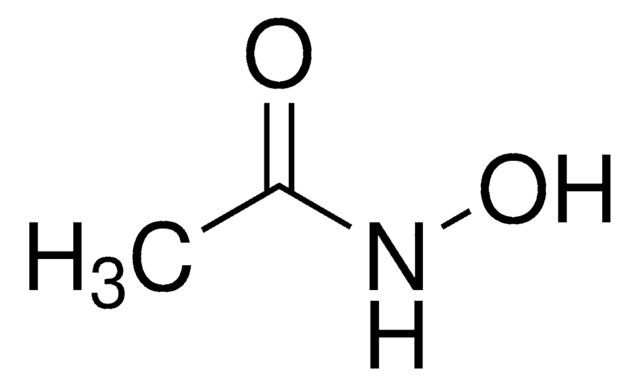
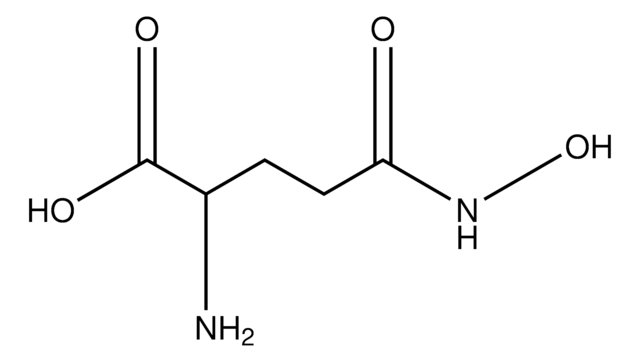
L-Aspartic acid β-hydroxamate
>98%
Synonym(s):
AAH, HDX, LAH
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C4H8N2O4
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
148.12
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352209
eCl@ss:
32160406
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.26
Recommended Products
Product Name
L-Aspartic acid β-hydroxamate, serine racemase inhibitor
Quality Level
Assay
>98%
form
powder
color
white to yellow
application(s)
detection
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
N[C@@H](CC(=O)NO)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H8N2O4/c5-2(4(8)9)1-3(7)6-10/h2,10H,1,5H2,(H,6,7)(H,8,9)/t2-/m0/s1
InChI key
ZBYVTTSIVDYQSO-REOHCLBHSA-N
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
N Thomasset et al.
International journal of cancer, 49(3), 421-424 (1991-09-30)
D and L isomers of aspartic acid beta-hydroxamate (respectively DAH and LAH) were compared for their in vitro and in vivo activity against the murine leukemia L5178Y and their tolerance in vivo in DBA/2 mice. DAH and LAH displayed comparable
Jie Zheng et al.
Nature communications, 8(1), 923-923 (2017-10-17)
The vitamin D receptor/retinoid X receptor-α heterodimer (VDRRXRα) regulates bone mineralization via transcriptional control of osteocalcin (BGLAP) gene and is the receptor for 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D
Daniel Sepúlveda-Crespo et al.
Nanomedicine : nanotechnology, biology, and medicine, 13(1), 49-58 (2016-08-27)
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is a major biomedical problem worldwide. Although new direct antiviral agents (DAAs) have been developed for the treatment of chronic HCV infection, the potential emergence of resistant virus variants and the difficulties to implement their
Lidia Mingorance et al.
PLoS pathogens, 14(9), e1007284-e1007284 (2018-09-19)
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection constitutes a significant health burden worldwide, because it is a major etiologic agent of chronic liver disease, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. HCV replication cycle is closely tied to lipid metabolism and infection by this virus
Eric R. Braverman
The Healing Nutrients Within: Facts, Findings, and New Research on Amino Acids null
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service