90100401
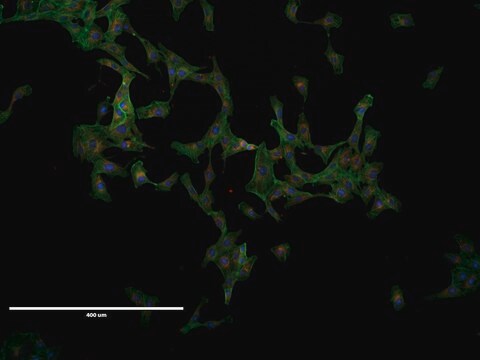
Aedes albopictus cell line
mosquito larvae, Epithelial
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
41106514
NACRES:
NA.81
biological source:
mosquito larvae
growth mode:
Adherent
karyotype:
Diploid
morphology:
Epithelial
products:
Not specified
receptors:
Not specified
Recommended Products
Product Name
Aedes albopictus cell line,
biological source
mosquito larvae
Quality Level
form
liquid
growth mode
Adherent
karyotype
Diploid
morphology
Epithelial
products
Not specified
receptors
Not specified
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−196°C
Cell Line Origin
Mosquito larvae
Cell Line Description
Derived from pooled newly hatched Aedes albopictus larvae. The cells are susceptible to a range of Mosquito borne viruses.
Application
Virus studies: Mosquito viruses
Culture Medium
EMEM (EBSS) + 2mM Glutamine + 1% Non Essential Amino Acids (NEAA) + 10% Foetal Bovine Serum (FBS).
Subculture Routine
Split sub-confluent cultures (70-80%) 1:3 to 1:6 i.e. seeding at 3x1,000 to 2x10,000 cells/cm2using
Other Notes
Additional freight & handling charges may be applicable for Asia-Pacific shipments. Please check with your local Customer Service representative for more information.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Propagation of arboviruses in Singh's Aedes cell lines. I. Growth of arboviruses in Aedes albopictus and A. aegypti cell lines.
K R Singh
Current topics in microbiology and immunology, 55, 127-133 (1971-01-01)
V K Jenkins et al.
International journal of radiation biology and related studies in physics, chemistry, and medicine, 50(2), 269-278 (1986-08-01)
In vitro effects of radiation were studied in two permanent cell lines (AGS and SII) from two patients with adenocarcinoma of the stomach and three permanent sublines from each cell line. Radiation survival parameters for AGS and SII parent cell
D F Young et al.
Virology, 365(1), 238-240 (2007-05-19)
Whilst screening various cell lines for their ability to respond to interferon (IFN), we noted that in comparison to other tissue culture cells AGS tumour cells, which are widely used in biomedical research, had very low levels of STAT1. Subsequent
S C Barranco et al.
Cancer research, 43(4), 1703-1709 (1983-04-01)
Ten permanent clones derived from a single biopsy specimen of an untreated human adenocarcinoma of the stomach were established and characterized in vitro. Tissue culture growth properties, doubling times, plating efficiencies, growth fractions, cell cycle phase distributions, DNA indices, modal
S C Barranco et al.
Investigational new drugs, 1(2), 117-127 (1983-01-01)
Four permanent clones of a human adenocarcinoma of the stomach and the parent line from which they were isolated were used as an in vitro model system to evaluate the effects of 8 anticancer agents on cell survival. The drugs
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service