MABF2117
Anti-insulin peptide–MHC Antibody, clone mAb287
clone mAb287, from mouse
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
eCl@ss:
32160702
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
antibody form
purified antibody
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
mAb287, monoclonal
species reactivity
mouse
packaging
antibody small pack of 25 μg
technique(s)
ELISA: suitable
flow cytometry: suitable
inhibition assay: suitable
isotype
IgG1κ
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
mouse ... Ins1(16333)
Related Categories
General description
Juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) is considered as an autoimmune disease where islet infiltration of T cells, B cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells leads to their progressive destruction. It is reported that non-obese diabetic mice (NOD) express a single MHC class II molecule, IAg7, which is shown to be essential for the development of IDDM. It is shown that the major T cell insulin epitope resides with in amino acids 9-23 of the beta chain (B:9-23) and this peptide can bind to IAg7 in multiple positions (registers). Pathogenic CD4 T cells can recognize beta 9-23:I Ag7 complex when the insulin peptide is bound in register 3 (R3), which places amino acids 14-22 of the beta chain in the core P1 to P9 position and places arginine at P9 position, which is highly unfavored for the IAg7 pocket. The binding motifs of IAg7 are degenerate and contain small hydrophobic residues at P4 and P6 position. This monoclonal antibody (clone mAb287) selectively binds to B:9-23 when presented by IAg7 only in R3. It blocks the binding of IAg7-B:10-23 R3 tetramers to cognate T cells and impedes T cell responses to soluble B:9-23 peptides, but does not affect recognition of any other peptide bound to IAg7. This antibody is also shown to diminish T cell infiltration in NOD mice, delay the development of IDDM and overt hyperglycemia. (Ref.: Stratmann, T., et al. (2000). J Immunol. 165(6); 3214-3225; Zhang, L., et al. (2014). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 111 (7); 2656-2661).
Specificity
Clone mAb287 is a mouse monoclonal antibody that recognizes a molecular complex of mouse MHC class II (named I-Ag7) and a peptide derived from insulin B-chain, amino acids 9-22.
Immunogen
Soluble I-Ag7 bearing Insulin R3 peptides.
Application
Anti-insulin peptide MHC, clone mAb287, Cat. No. MABF2117, is a mouse monoclonal antibody that detects Insulin peptide -MHC and has been tested for use in ELISA, Flow Cytometry, and Inhibition assay.
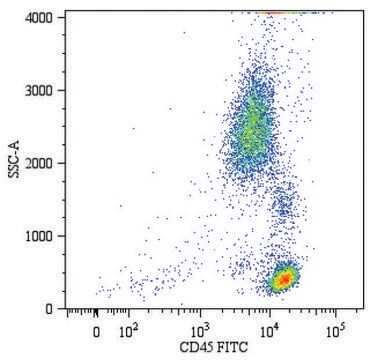
Flow Cytometry Analysis: A representative lot detected insulin peptide MHC in Flow Cytometry applications (Zhang, L., et. al. (2014). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111(7):2656-61).
ELISA Analysis: A representative lot detected insulin peptide MHC in ELISA applications (Zhang, L., et. al. (2014). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111(7):2656-61).
Inhibition Analysis: A representative lot of this antibody inhibited in vitro responses of insulin-specific T-cell hybridomas/transfectomas. (Zhang, L., et. al. (2014). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111(7):2656-61).
ELISA Analysis: A representative lot detected insulin peptide MHC in ELISA applications (Zhang, L., et. al. (2014). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111(7):2656-61).
Inhibition Analysis: A representative lot of this antibody inhibited in vitro responses of insulin-specific T-cell hybridomas/transfectomas. (Zhang, L., et. al. (2014). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111(7):2656-61).
Research Category
Signaling
Signaling
Quality
Evaluated by Isotype testing,
Physical form
Format: Purified
Protein G purified
Purified mouse monoclonal antibody IgG1 in PBS without preservatives.
Storage and Stability
Stable for 1 year at -20°C from date of receipt. Handling Recommendations: Upon receipt and prior to removing the cap, centrifuge the vial and gently mix the solution. Aliquot into microcentrifuge tubes and store at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles, which may damage IgG and affect product performance.
Other Notes
Concentration: Please refer to lot specific datasheet.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Pimploy Rattanaamnuaychai et al.
Heliyon, 6(9), e04951-e04951 (2020-10-01)
β-cell dedifferentiation has been accounted as one of the major mechanisms for β-cell failure; thus, is a cause to diabetes. We study direct impacts of liraglutide treatment on ex vivo human dedifferentiated islets, and its effects on genes important in
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service