MABE1820
Anti-Neurofibromin C Antibody, clone NFC
clone NFC, from mouse
Synonym(s):
Neurofibromatosis-related protein NF-1
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
eCl@ss:
32160702
NACRES:
NA.41
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
NFC, monoclonal
species reactivity
human
packaging
antibody small pack of 25 μL
technique(s)
immunohistochemistry: suitable (paraffin)
isotype
IgG1κ
UniProt accession no.
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... NF1(4763)
Related Categories
General description
Neurofibromin (UniProt: P21359; also known as Neurofibromatosis-related protein NF-1) is encoded by the NF1 gene (Gene ID: 4763) in human. Neurofibromin is a GTPase-activating protein that negatively regulatres RAS/MAOK pathway by enhancing the hydrolysis of Ras-bound GTP. Hence, it can display tumor suppressor properties. Neurofibromin has been detected in brain, peripheral nerves, lung, colon, and muscle tissues. It has a CRAL-TRIO domain (aa 1580-1738) that facilitates its binding to phospholipids. It binds primarily glycerophospholipids with monounsaturated C18:1 and/or C16:1 fatty acid moieties and a phosphatidylethanolamine or phosphatidylcholine head group. Neurofibromin also has a Ras-GTP domain (aa 1235-1451). Mutations in NF1 gene are known to cause Neurofibromatosis type I that involved tumors in the peripheral nervous system and fibromatous skin tumors. Some mutations are also known to cause colorectal cancer and juvenile leukemia. Six different isoforms of Neurofibromin have been described that are produced by alternative splicing. (Ref.: Rossi, S., et al. (2018). Mod. Pathol. 31(1), 160-168).
Specificity
Clone NFC specifically detects human Neurofibromin C. it targets an epitope with in the C-terminal region.
Immunogen
Epitope: C-terminus
Recombinant fragment corresponding to 281 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human Neurofibromin C.
Application
Anti-Neurofibromin C, clone NFC, Cat. No. MABE1820, is a highly specific mouse monoclonal antibody that targets Neurofibromin and has been tested for use in Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin).
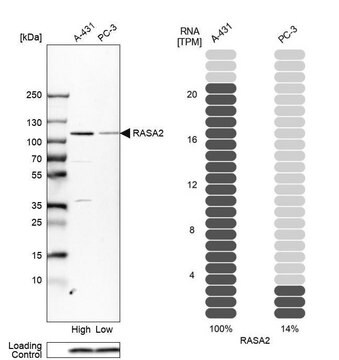
Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) Analysis: A representative lot detected Neurofibromin C in Immunohistochemistry applications (Rossi, S., et. al. (2018). Mod Pathol. 31(1):160-168).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected Neurofibromin C lysate from human NF1 +/+ cells, but not in -/- cells or NF1+/+ cells transfected with siRNA targeting neurofibromin (Reuss, DE.,et al., (2014). Acta Neuropathol. 127(4); 565-572).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected Neurofibromin C lysate from human NF1 +/+ cells, but not in -/- cells or NF1+/+ cells transfected with siRNA targeting neurofibromin (Reuss, DE.,et al., (2014). Acta Neuropathol. 127(4); 565-572).
Research Category
Epigenetics & Nuclear Function
Epigenetics & Nuclear Function
Quality
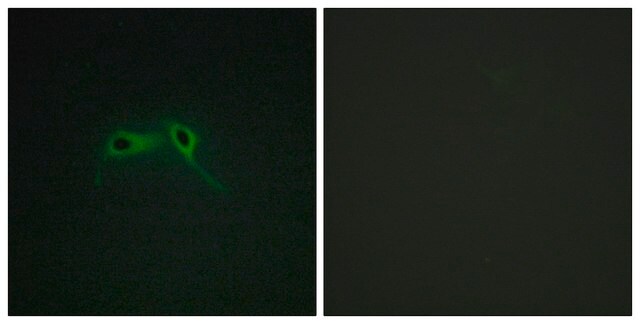
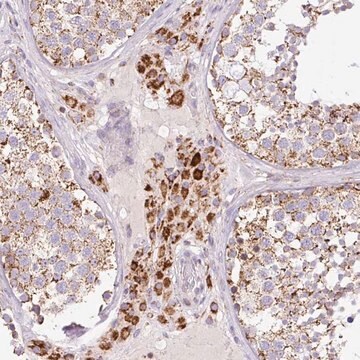
Evaluated by Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) in human kidney tissue sections.
Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) Analysis: A 1:50 dilution of this antibody detected Neurofibromin C in human kidney tissue sections.
Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) Analysis: A 1:50 dilution of this antibody detected Neurofibromin C in human kidney tissue sections.
Target description
319.37 kDa calculated.
Physical form
Format: Purified
Protein G purified
Purified mouse monoclonal antibody IgG1 in buffer containing 0.1 M Tris-Glycine (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl with 0.05% sodium azide.
Storage and Stability
Stable for 1 year at 2-8°C from date of receipt.
Other Notes
Concentration: Please refer to lot specific datasheet.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Sabrina Rossi et al.
Modern pathology : an official journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, Inc, 31(1), 160-168 (2017-09-02)
An increasing body of evidence supports the involvement of NF1 mutations, constitutional or somatic, in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs). Due to the large size of the NF1 locus, the existence of multiple pseudogenes and the wide spectrum
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service