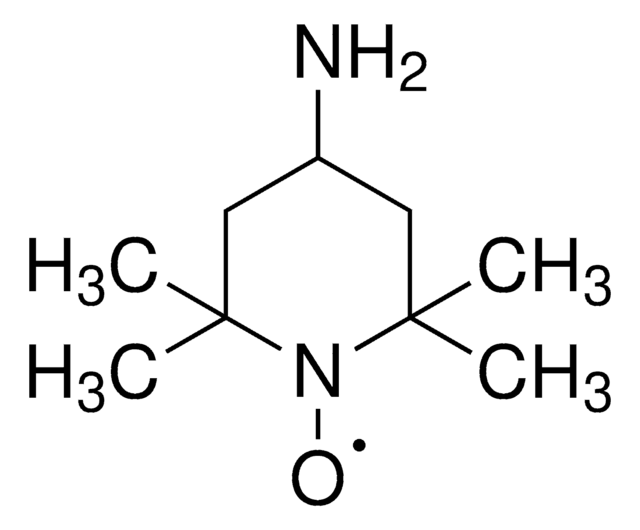
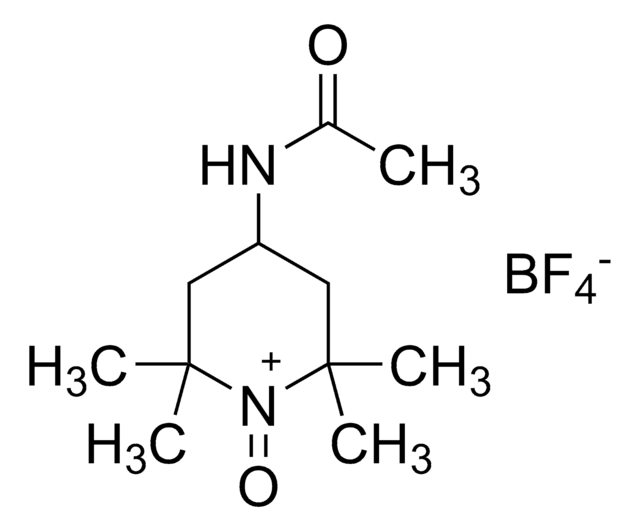
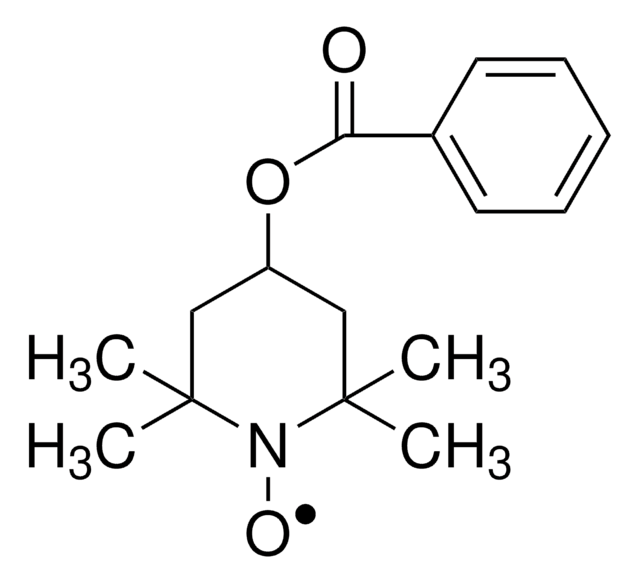
About This Item
Recommended Products
Assay
90%
form
powder
reaction suitability
reagent type: oxidant
mp
182-189 °C (D)
storage temp.
2-8°C
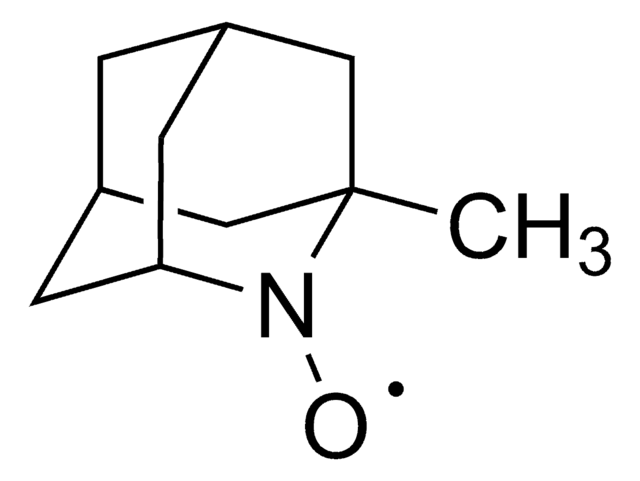
SMILES string
[O]N1[C@@H]2C[C@H]3C[C@@H](C2)C[C@@H]1C3
InChI
1S/C9H14NO/c11-10-8-2-6-1-7(4-8)5-9(10)3-6/h6-9H,1-5H2/t6-,7+,8-,9+
InChI key
BCJCJALHNXSXKE-SPJNRGJMSA-N
Related Categories
General description
Application
- As catalyst for the oxidation of wood cellulose.
- As catalyst in the total synthesis of Yaku′amide A, a potential cytotoxin obtained from sponge Ceratopsion sp.
- As oxidant for the oxidation of (S)-glycidol.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
TEMPO (2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidinyloxy or 2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidine 1-oxyl) and its derivatives are stable nitroxy radicals used as catalysts in organic oxidation reactions. TEMPO was discovered by Lebedev and Kazarnovskii in 1960. The stable free radical nature of TEMPO is due to the presence of bulky substituent groups, which hinder the reaction of the free radical with other molecules.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service![9-Azabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane N-oxyl 95%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/287/155/e2f4a2e1-1d4e-4bed-9187-9e16d23cbbbf/640/e2f4a2e1-1d4e-4bed-9187-9e16d23cbbbf.png)