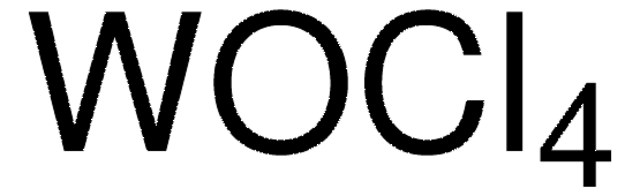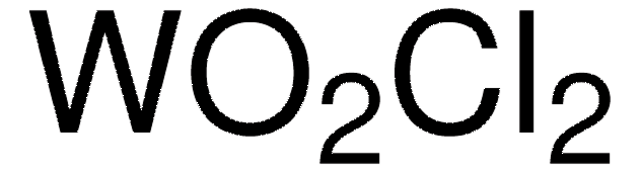373729
Molybdenum(VI) tetrachloride oxide
97%
Synonym(s):
Molybdenum chloride oxide, Molybdenum oxide chloride, Molybdenum oxytetrachloride, Molybdenum tetrachloride monoxide, Molybdenum(VI) oxychloride, Tetrachlorooxomolybdenum
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
97%
form
powder or crystals
reaction suitability
reagent type: catalyst
core: molybdenum
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
Cl[Mo](Cl)(Cl)(Cl)=O
InChI
1S/4ClH.Mo.O/h4*1H;;/q;;;;+4;/p-4
InChI key
UYEGPKGLVUUIGD-UHFFFAOYSA-J
Application
- To prepare a binary metal catalyst (MoOCl4-n-BuLi) for the living polymerization of various acetylenes.
- As an oxidant in the aromatization of various Hantzsch-1,4-dihydropyridines.
- As a molybdenum (Mo) precursor to prepare nafion-Mo composite material, which is used as a catalyst for the preparation of nitrones by reacting primary amines with aldehydes.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Skin Corr. 1B
Storage Class Code
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Advances in materials have often been led by the development of new synthetic methods that provide control over size, morphology and structure.
Advances in materials have often been led by the development of new synthetic methods that provide control over size, morphology and structure. The preparation of materials in a scalable and continuous manner is critical when development moves beyond lab-scale quantities.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service