SAE0091
Lisostafina from Staphylococcus staphylolyticus
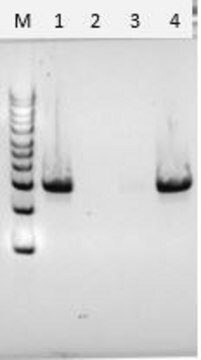
free of DNA contaminants, ≥500 units/mg protein, lyophilized powder, suitable for Microbiome research
Sinónimos:
Endopeptidasa glicil-glicina
About This Item
Productos recomendados
product name
Lisostafina from Staphylococcus staphylolyticus, free of DNA contaminants, suitable for Microbiome research, lyophilized powder, ≥500 units/mg protein
biological source
microbial (Staphylococcus staphylotyticus)
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
≥500 units/mg protein
mol wt
27 kDa
feature
DNA free
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Application
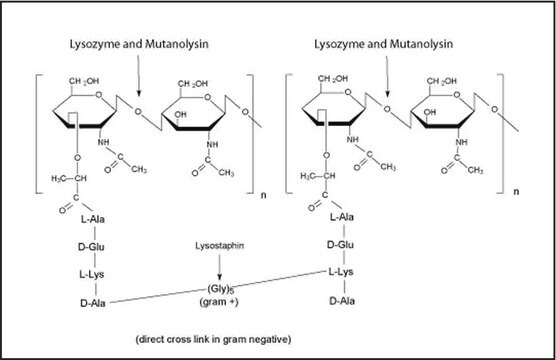
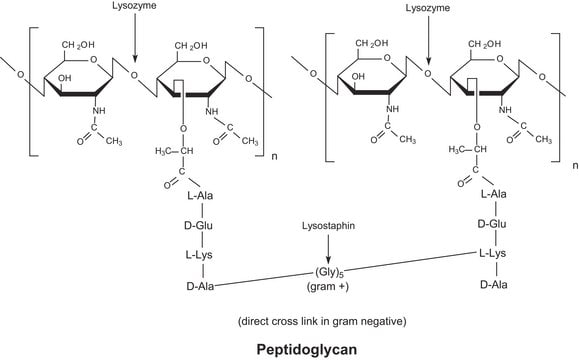
Lysostaphin is a zinc metalloenzyme isolated from a bacterial culture of Staphylococcus staphylolyticus. It has specific lytic action against other Staphylococcus species, including S. aureus.1,2 Lysostaphin has
hexosaminidase, amidase, and endopeptidase activities. It cleaves polyglycine crosslinks in the cellular wall which leads to cell lysis of Staphylococcus species, but not of other bacterial genera. [Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3(4), 1139-1161]
Lysostaphin is a single polypeptide chain of 246 amino acids, a molecular mass of 26,926 Da, isoelectric point of 9.5, (5) and an activity pH optimum of 7.5.(6)
Biochem/physiol Actions
pH de actividad óptimo: ~7,5
Unit Definition
Physical form
signalword
Danger
hcodes
pcodes
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Artículos
An overview of human microbiome research, workflow challenges, sequencing, library production, data analysis, and available microbiome reagents to support your research.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico