S9697
Superoxide Dismutase bovine
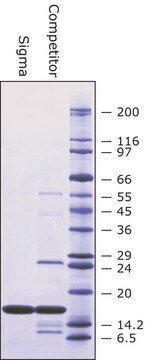
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, lyophilized powder, ≥2500 units/mg protein, ≥90% (SDS-PAGE)
Sinónimos:
Superoxide Dismutase 1 bovine, cytocuprein, erythrocuprein, hemocuprein, CU/ZN-SOD, SOD, SOD1, Superoxide: superoxide oxidoreductase
About This Item
Productos recomendados
biological source
bovine
Quality Level
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
assay
≥90% (SDS-PAGE)
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
≥2500 units/mg protein
storage condition
(Tightly closed)
technique(s)
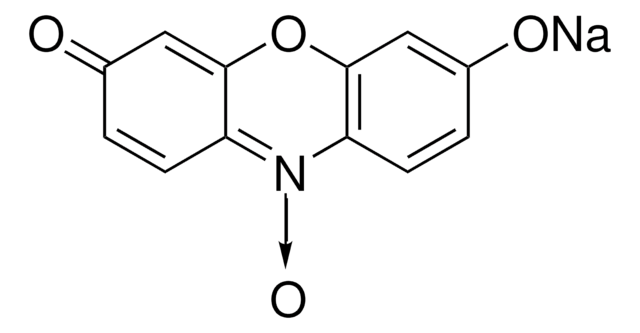
inhibition assay: suitable
color
white
optimum pH
7.8 (25 °C)
pH range
7.6-10.5
pI
4.95
sequence note
MATKAVCVLKGDGPVQGTIHFEAKGDTVVVTGSITGLTEGDHGFHVHQFGDNTQGCTSAGPHFNPLSKKHGGPKDEERHVGDLGNVTADKNGVAIVDIVDPLISLSGEYSIIGRTMVVHEKPDDLGRGGNEESTKTGNAGSRLACGVIGIAK
UniProt accession no.
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
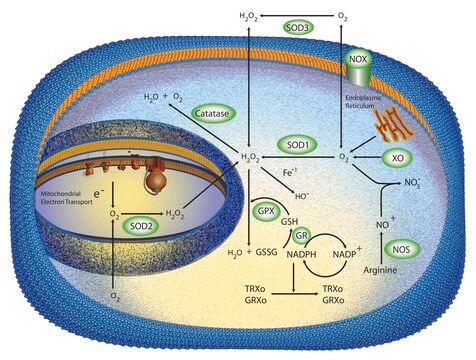
SOD from bovine erythrocytes was the first SOD to be found in mammalian tissues. There are three forms of SOD differentiated by the metal ions in the active site. These are Cu+2/Zn+2, Mn+2, and Fe+2 SOD. In vertebrates, Cu/Zn-SOD is found in the cytoplasm, chloroplast, and may be in extracellular space, while Mn-SOD is found in the mitochondrial matrix space and peroxisome. Fe-SOD is found in the chloroplast of prokaryotes and some higher plants.
Application
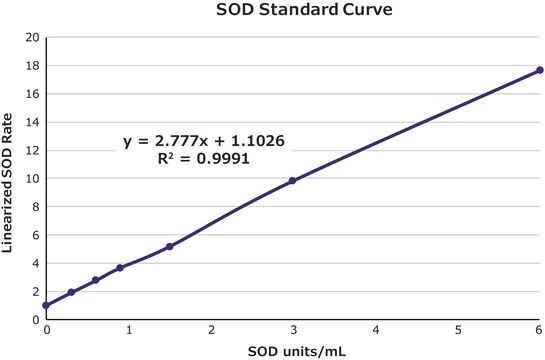
- to construct a calibration curve for the evaluation of superoxide dismutase (SOD) enzyme activities
- in a study to investigate where lipoproteins may affect the L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway
- in a study to investigate the mass spectral evidence for carbonate-anion-radical-induced posttranslational modification of tryptophan to kynurenine in human Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase
Biochem/physiol Actions
Unit Definition
Preparation Note
Reconstitution
Analysis Note
SOD has no significant absorbance peak at 280 nM because of the absence of tryptophan.
Other Notes
Antibody
Related product
signalword
Danger
hcodes
pcodes
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Artículos
Oxidative stress is mediated, in part, by reactive oxygen species produced by multiple cellular processes and controlled by cellular antioxidant mechanisms such as enzymatic scavengers or antioxidant modulators. Free radicals, such as reactive oxygen species, cause cellular damage via cellular.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico