J2000
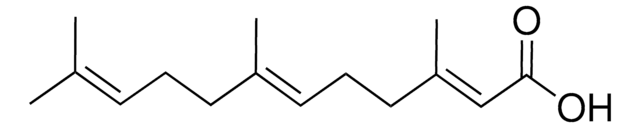
Juvenile hormone III
≥65%, liquid, non-sterile
Sinónimos:
Methyl farnesoate, 10,11-epoxide, C16-Juvenile Hormone, JH-III, Manduca hormone, trans,trans-10,11-Epoxy-3,7,11-trimethyl-2,6-dodecadienic acid methyl ester
About This Item
Productos recomendados
biological source
synthetic (organic)
Quality Level
sterility
non-sterile
assay
≥65% (HPLC)
form
liquid
concentration
≥65%
technique(s)
activity assay: suitable
shipped in
ambient
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
COC(=O)\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC[C@H]1OC1(C)C
InChI
1S/C16H26O3/c1-12(9-10-14-16(3,4)19-14)7-6-8-13(2)11-15(17)18-5/h7,11,14H,6,8-10H2,1-5H3/b12-7+,13-11+
InChI key
QVJMXSGZTCGLHZ-ZPLWXOMKSA-N
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
General description
Juvenile hormone III (JH III) is the most prevalent juvenile hormone (JH) found in insects.
Application
- study the effect of juvenile hormone on mictic (sexual) female production of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis Muller
- study the effect of juvenile hormone on head GB19811 (putative Takeout/juvenile hormone binding protein) mRNA levels in adult honeybees
- study the effect of juvenile hormone on gonadotropic and physiological functions in bumblebee Bombus terrestris
Biochem/physiol Actions
inhibitor
related product
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Chronic 4
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico