GS90
GST T1-1, Recombinant Human
Sinónimos:
glutathione S-transferase theta 1
About This Item
Productos recomendados
biological source
human
Quality Level
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
assay
95% (SDS-PAGE)
form
frozen liquid
specific activity
8.8 units/mg protein (as assayed by the spectrophotometric determination of NADPH oxidation coupled to the glutathione peroxidase activity of GST T1-1 on cumene hydroperoxide (1.5 mM) in the presence of reduced glutathione (1 mM) in 100 mM NaPO4 (pH 7.0) at room temperature.)
mol wt
25 kDa
concentration
1.95 mg/mL
storage temp.
−70°C
Gene Information
human ... GSTT1(2952)
General description
Biochem/physiol Actions
Storage and Stability
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico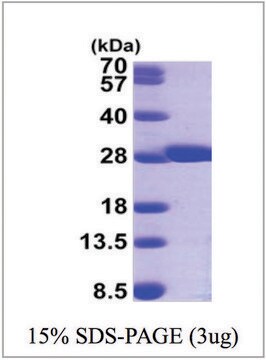

![[1,1′-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene]dichloropalladium(II)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/130/734/8846aa26-1858-458a-998d-8c306c13bf0f/640/8846aa26-1858-458a-998d-8c306c13bf0f.png)