F9291
ANTI-FLAG® M2 monoclonal antibody produced in mouse
clone M2, purified immunoglobulin, buffered aqueous glycerol solution
Sinónimos:
Anti-ddddk, Anti-dykddddk
About This Item
Productos recomendados
biological source
mouse
conjugate
biotin conjugate
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
M2, monoclonal
form
buffered aqueous glycerol solution
species reactivity
all
concentration
~1 mg/mL
technique(s)
dot blot: suitable (chemiluminescent detection)
isotype
IgG1
immunogen sequence
DYKDDDDK
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
General description
Application
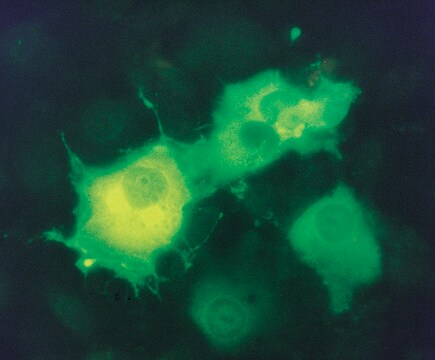
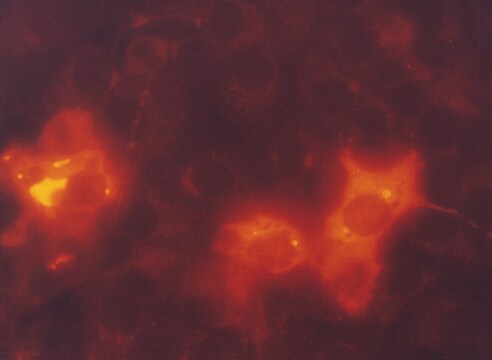
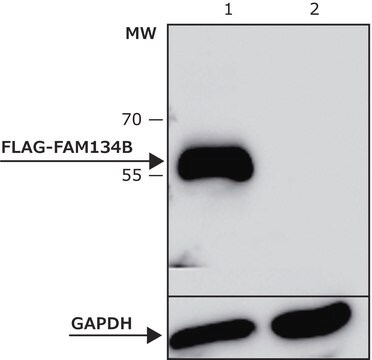
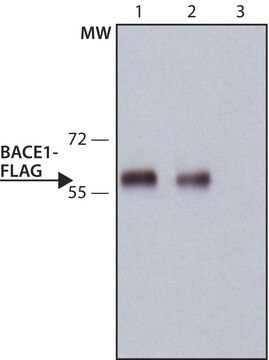
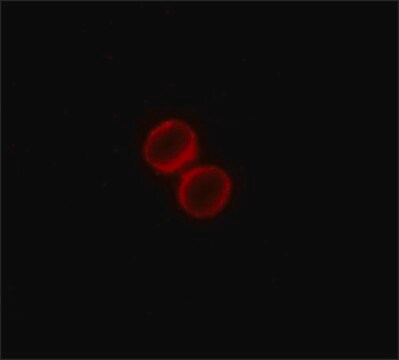
Antibody is suitable for immunofluorescence, western blotting, microscopy applications and for the formation of avidin-biotin complexes.
Learn more product details in our FLAG® application portal.
Physical form
Preparation Note
Legal Information
¿No encuentra el producto adecuado?
Pruebe nuestro Herramienta de selección de productos.
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 2
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico