A8131
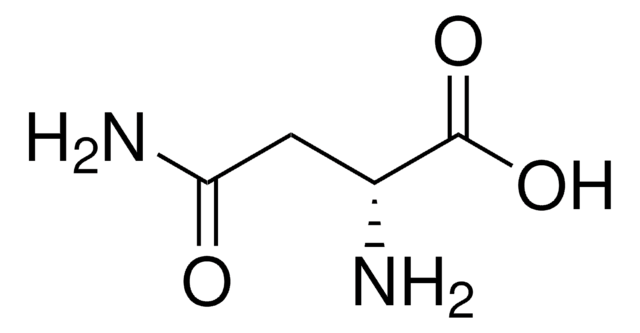
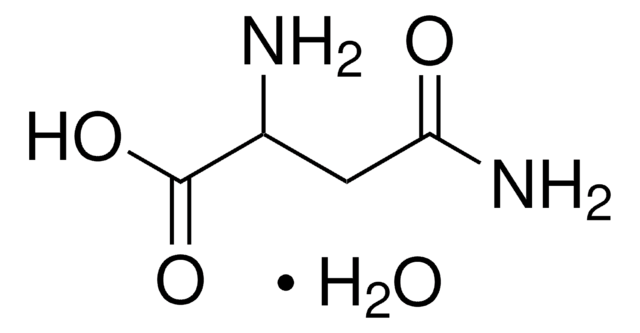
D-Asparagine monohydrate
≥99% (TLC)
Sinónimos:
(R)-(-)-2-Aminosuccinamic acid, (R)-2-Aminosuccinic acid 4-amide, (D)-Aspartic acid 4-amide
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Nombre del producto
D-Asparagine monohydrate, ≥99% (TLC)
Quality Level
assay
≥99% (TLC)
form
powder or crystals
color
white to off-white
mp
275 °C (dec.) (lit.)
application(s)
peptide synthesis
SMILES string
NC(C[C@@H](N)C(O)=O)=O.[H]O[H]
InChI
1S/C4H8N2O3.H2O/c5-2(4(8)9)1-3(6)7;/h2H,1,5H2,(H2,6,7)(H,8,9);1H2/t2-;/m1./s1
InChI key
RBMGJIZCEWRQES-HSHFZTNMSA-N
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Chromatograms
application for HPLCNuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico