67563
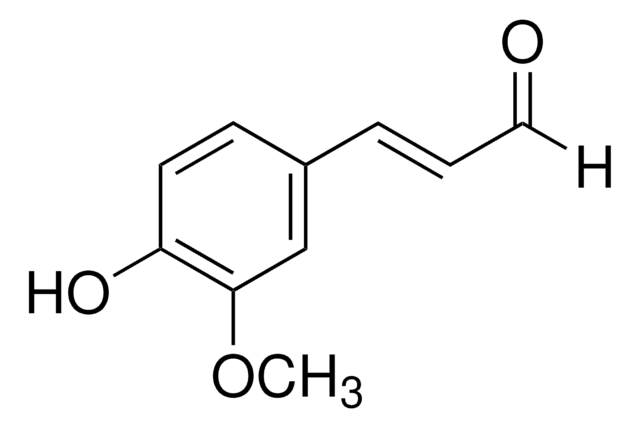
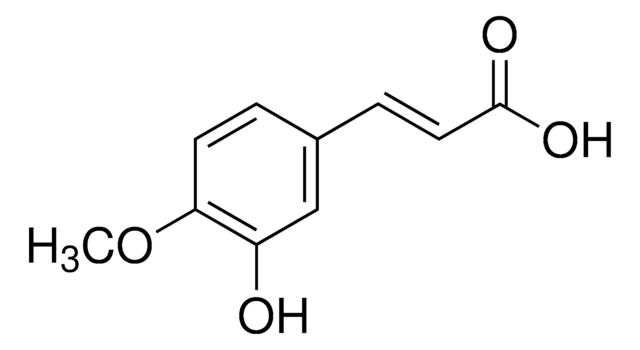
3,4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxycinnamic acid
≥95.0% (HPLC)
Sinónimos:
3-(3,4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxyphenyl)-2-propenoic acid, 3-Methoxycaffeic acid, 5-Hydroxyferulic acid
About This Item
Productos recomendados
assay
≥95.0% (HPLC)
form
solid
application(s)
metabolomics
vitamins, nutraceuticals, and natural products
SMILES string
COc1cc(\C=C\C(O)=O)cc(O)c1O
InChI
1S/C10H10O5/c1-15-8-5-6(2-3-9(12)13)4-7(11)10(8)14/h2-5,11,14H,1H3,(H,12,13)/b3-2+
InChI key
YFXWTVLDSKSYLW-NSCUHMNNSA-N
Categorías relacionadas
Biochem/physiol Actions
Packaging
signalword
Warning
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
target_organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico