C2-BIOC
Collagenase Type II, Cls II
Sinónimos:
Collagen A
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.78
Productos recomendados
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
General description
Collagenase Type II (Cls II) is one of the main tissue dissociation enzymes produced by Clostridium histolyticum. It aids to digest the smaller collagen fragments produced by Type I collagenase. Collagenases, a member of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMPs) family, digests collagen in the extracellular matrix (ECM). Collagens are triple helix structural proteins comprising three collagen polypeptides with high tensile strength.
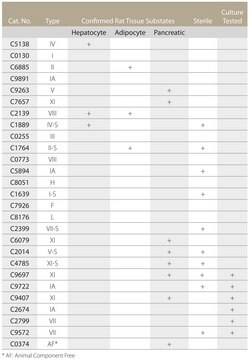
This product is identical to Biochrom GmbH part numbers C2-22 and C2-28. Enzyme blending from collagenase, clostripain, with tryptic and proteolytic activities from Clostridium histolyticum. This preparation shows a high clostripain activity with the tryptic activity close to type I. Suitable for liver, bone, thyroid, heart, and salivary gland tissue. Specific activity is 125 to 250 Mandl units per milligram of powdered substance.
Application
Collagenase Type II (Cls II) has been used:
- as a component of Roswell park memorial Institute (RPMI)-1640 media to digest hepatic tissues
- to perfuse murine heart for the isolation of epicardial stromal cells (EpiSC)
- to digest collagenase and inject it into the intrarenal aorta abdominalis to perfuse the kidneys
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documentos section.
Si necesita más asistencia, póngase en contacto con Atención al cliente
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Tissue dissociation enzymes for adipose stromal vascular fraction cell isolation: a review
Lockhart RA, et al.
Journal of stem cell research & therapy (2015)
Lukas Peintner et al.
Autophagy, 17(9), 2384-2400 (2020-09-25)
Mutations in the PKD1 gene result in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), the most common monogenetic cause of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) in humans. Previous reports suggested that PKD1, together with PKD2/polycystin-2, may function as a receptor-cation channel complex
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico