AB5204
Anti-Sodium Channel Antibody, Voltage Gated, Brain Type I
Chemicon®, from rabbit
Sinónimos:
Nav1.1, SCN1A
About This Item
WB
western blot: suitable
Productos recomendados
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
antibody form
affinity purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
purified by
affinity chromatography
species reactivity
mouse, rat
manufacturer/tradename
Chemicon®
technique(s)
immunohistochemistry: suitable
western blot: suitable
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... SCN1A(6323)
Specificity
SPECIES REACTIVITIES: It is expected that the antibody may also react with human due to sequence homology. Other species have not been tested.
Immunogen
Application
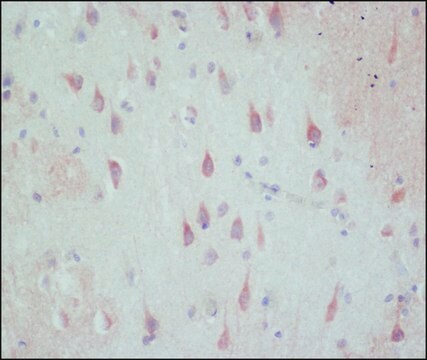
Western blot: 1:200 using ECL on rat brain membranes.
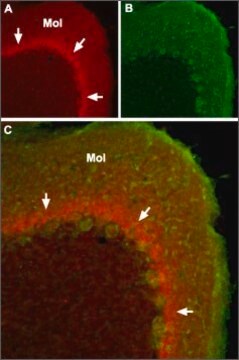
Immunohistochemistry on rat brain fixed frozen sections and mouse heart tissue.
Dilutions should be made using a carrier protein such as BSA (1-3%)
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by the end user.
Other Notes
Legal Information
¿No encuentra el producto adecuado?
Pruebe nuestro Herramienta de selección de productos.
hcodes
pcodes
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Chronic 3
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico