586005
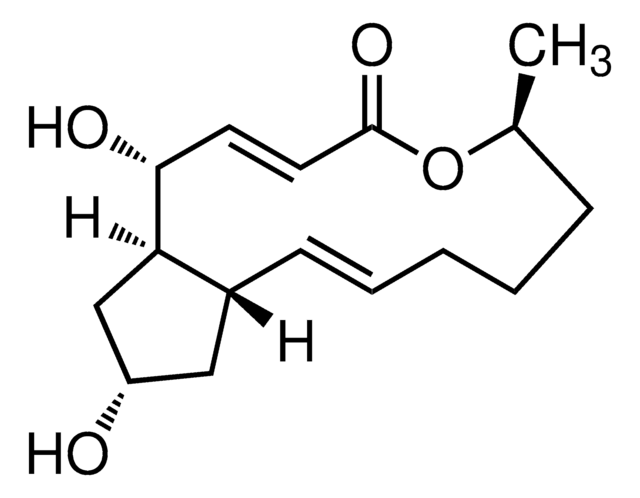
Thapsigargin
≥97% (TLC), solid, endoplasmic reticular Ca2+-ATPase inhibitor, Calbiochem®
Sinónimos:
Thapsigargin - CAS 67526-95-8 - Calbiochem
About This Item
Productos recomendados
product name
Thapsigargin - CAS 67526-95-8 - Calbiochem, Thapsigargin, CAS 67526-95-8, is a cell-permeable, tumor-promoting sesquiterpene lactone that releases calcium by non-competitvley inhibiting endoplasmic reticular Ca2+-ATPase (IC₅₀ = 4-13 nM).
Quality Level
assay
≥97% (TLC)
form
solid
manufacturer/tradename
Calbiochem®
storage condition
OK to freeze
protect from light
color
colorless
solubility
DMSO: >1 mg/mL
ethanol: 5 mg/mL
shipped in
ambient
storage temp.
−20°C
InChI
1S/C34H50O12/c1-9-12-13-14-15-17-24(37)43-28-26-25(20(5)27(28)44-30(38)19(4)11-3)29-34(41,33(8,40)31(39)45-29)22(42-23(36)16-10-2)18-32(26,7)46-21(6)35/h11,22,26-29,40-41H,9-10,12-18H2,1-8H3/b19-11-/t22-,26+,27-,28-,29-,32-,33+,34+/m0/s1
InChI key
IXFPJGBNCFXKPI-FSIHEZPISA-N
General description
Biochem/physiol Actions
endoplasmic reticular Ca2+ ATPase
Warning
Reconstitution
Other Notes
Won, J.G. and Orth, D.N. 1995. Endocrinology 136, 5399.
Tepel, M., et al. 1994. Biochim. Biophys. Acta1220, 248.
Begum, N., et al. 1993. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 3352.
Low, A.M., et al. 1993. Eur. J. Pharmacol.230, 53.
Tsukamoto, A. and Karneko, Y. 1993. Cell. Biol. Int.17, 969.
Wong, W.L., et al. 1993. Biochem. J.289, 71.
Glennon, M.C., et al. 1992. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 25568.
Xu, Y., et al. 1992. J. Neurochem.59, 2224.
Mason, M.J., et al. 1991. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 20856.
Thastrup, O., et al. 1990. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA87, 2466.
Legal Information
signalword
Danger
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
target_organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico