911798
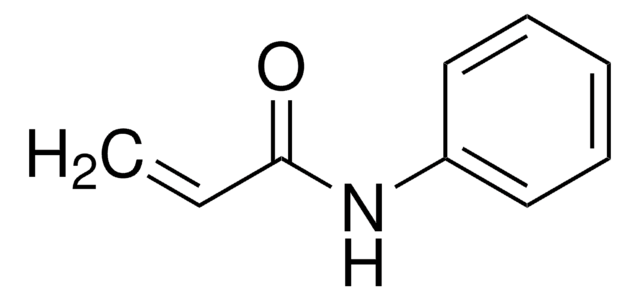
N-(4-Bromophenyl)-N-phenylacrylamide
≥95%
Sinónimos:
Electrophilic scout fragment, KB05, Scout fragment for targetable cysteine
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Quality Level
assay
≥95%
form
(Powder or crystals or solid or chunks)
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
Brc1ccc(cc1)N(c2ccccc2)C(=O)C=C
InChI
1S/C15H12BrNO/c1-2-15(18)17(13-6-4-3-5-7-13)14-10-8-12(16)9-11-14/h2-11H,1H2
InChI key
WFQQVUPOAKOTGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Application
Other Notes
Legal Information
Related product
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
Certificados de análisis (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documentos section.
Si necesita más asistencia, póngase en contacto con Atención al cliente
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Artículos
Ligandability describes the propensity of a protein target to bind a small molecule with high affinity. It is a precursor to evaluating druggability, which requires more advanced translational pharmacological effects and drug-like properties in vivo.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico