799009
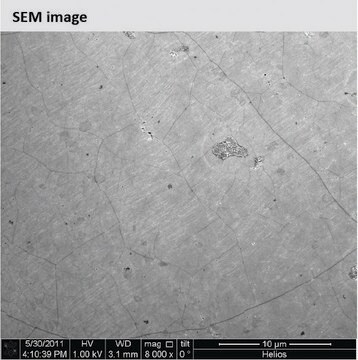
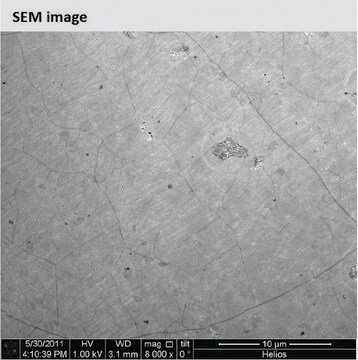
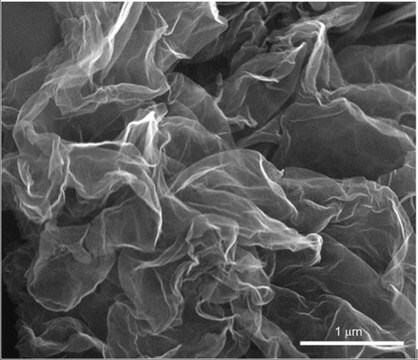
Graphene, monolayer film
1 in x 1 in on copper foil, avg. no. of layers, 1
Sinónimos:
Graphene/Cu
About This Item
Productos recomendados
product name
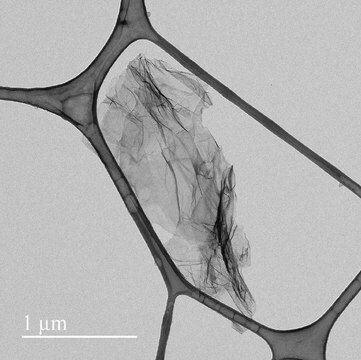
Monolayer graphene film, 1 in x 1 in on copper foil, avg. no. of layers, 1
Quality Level
description
Coverage: >95%
FET Electron Mobility on Al2O3: 2;000 cm2/V·s
FET Electron Mobility on SiO2/Si (expected): 4; 000 cm2/V·s
Grain size: Up to 10 μm
Number of graphene layers: 1
Transparency: >97%
form
film
feature
avg. no. of layers 1
resistance
350 Ω/sq
L × W × thickness
1 in. × 1 in. × (theoretical) 0.245 nm, monolayer graphene film
1 in. × 1 in. × 18 μm, copper foil substrate
color
transparent
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
General description
Transfer Method: Clean transfer method
Quality Control: Optical Microscopy & Raman checked
Application
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Artículos
Advanced technologies for energy conversion and storage are widely sought after for their potential to improve consumer and electronic device performance as well as for the prospect of reducing the societal and environmental impact of energy generation.
The production of hydrogen by catalytic water splitting is important for a wide range of industries including renewable energy petroleum refining and for the production of methanol and ammonia in the chemical industry.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico