730327
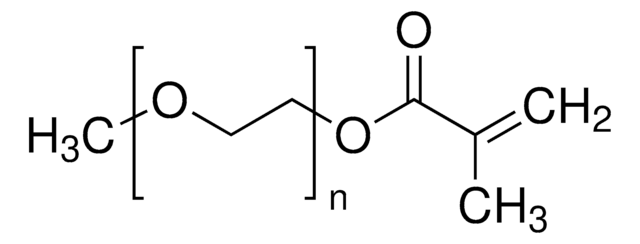
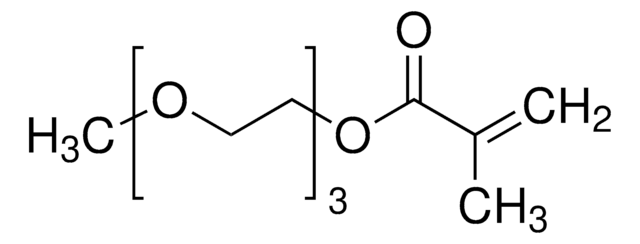
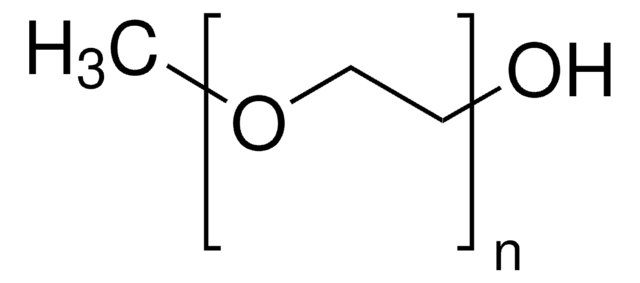
Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate
average Mn 4,000, methacrylate, methoxy, ≤300 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor
Sinónimos:
Polyethylene glycol, Methoxy PEG methacrylate, Methoxy poly(ethylene glycol) monomethacrylate, Poly(ethylene glycol) monomethyl ether monomethacrylate
About This Item
Productos recomendados
product name
Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate, average Mn 4,000, contains ≤300 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
form
powder or crystals
Quality Level
mol wt
average Mn 4,000
contains
≤300 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
reaction suitability
reagent type: chemical modification reagent
reaction type: Polymerization Reactions
transition temp
Tm 56-61 °C
density
1.100 g/cm3
Mw/Mn
<1.1
Ω-end
methacrylate
α-end
methoxy
polymer architecture
shape: linear
functionality: monofunctional
storage temp.
−20°C
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Categorías relacionadas
Preparation Note
signalword
Warning
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT SE 3
target_organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
>230.0 °F - closed cup
flash_point_c
> 110 °C - closed cup
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
Certificados de análisis (COA)
¿No ve la versión correcta?
Si necesita una versión concreta, puede buscar un certificado específico por el número de lote.
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Artículos
Progress in biotechnology fields such as tissue engineering and drug delivery is accompanied by an increasing demand for diverse functional biomaterials. One class of biomaterials that has been the subject of intense research interest is hydrogels, because they closely mimic the natural environment of cells, both chemically and physically and therefore can be used as support to grow cells. This article specifically discusses poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogels, which are good for biological applications because they do not generally elicit an immune response. PEGs offer a readily available, easy to modify polymer for widespread use in hydrogel fabrication, including 2D and 3D scaffold for tissue culture. The degradable linkages also enable a variety of applications for release of therapeutic agents.
Devising biomaterial scaffolds that are capable of recapitulating critical aspects of the complex extracellular nature of living tissues in a threedimensional (3D) fashion is a challenging requirement in the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico