S7571
Superoxide Dismutase from bovine erythrocytes
lyophilized powder, ≥3,000 units/mg protein, Protein ≥95 % by biuret
Synonym(s):
CU/ZN-SOD, Superoxide Dismutase 1 bovine, cytocuprein, erythrocuprein, hemocuprein, SOD, Superoxide: superoxide oxidoreductase
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
bovine
Quality Level
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
≥3,000 units/mg protein
mol wt
32.5 kDa
composition
Protein, ≥95% biuret
storage condition
(Store under nitrogen.
Tightly closed. Dry.)
greener alternative product characteristics
Atom Economy
Design for Energy Efficiency
Use of Renewable Feedstocks
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
technique(s)
immunoblotting: suitable
inhibition assay: suitable
color
blue-green
pI
4.95
solubility
water: 20 mg/mL
aqueous buffer, pH 7.5: soluble
application(s)
diagnostic assay manufacturing
greener alternative category
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
cow ... SOD1(281495) , SOD2(281496)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) is a redox-active metalloenzyme expressed in both aerobic and anaerobic living organisms. Bovine superoxide dismutase or CuZn SOD is a homodimer with each subunit containing one zinc and one copper ion.
Application
- in a study to assess a kinetic model of radiation-induced inactivation of superoxide dismutase in nitrous oxide-saturated solutions
- in a study to investigate the possible participation of superoxide anion in the intestinal tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase reaction
- to investigate its effect on the hemolysis rate of human RBCs and hemoglobin-nitric oxide complex (HbNO) stability in human erythrocytes
- in combination with catalase to study its effect on cell differentiation in vitro
- to quantify superoxide levels and study their effect on reactivity in mouse pulmonary arteries through chemiluminescence and cytochrome C reduction methods
Biochem/physiol Actions
Unit Definition
Physical form
Application
related product
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
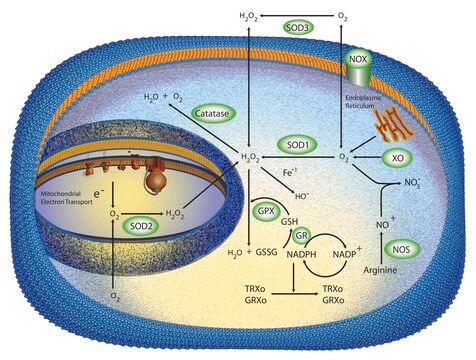
Oxidative stress is mediated, in part, by reactive oxygen species produced by multiple cellular processes and controlled by cellular antioxidant mechanisms such as enzymatic scavengers or antioxidant modulators. Free radicals, such as reactive oxygen species, cause cellular damage via cellular.
Protocols
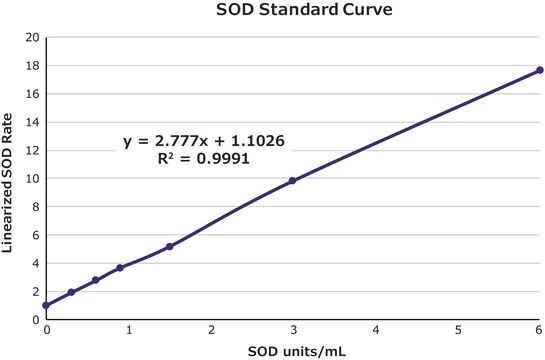
Enzymatic Assay of Superoxide Dismutase
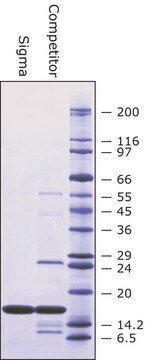
Separation of Superoxide dismutase
Chromatograms
application for HPLCOur team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service