P1146
Phosphatase, Acid from potato
lyophilized powder, ≥3.0 units/mg solid
Synonym(s):
(Orthophosphoric-monoester phosphohydrolase acid optimum), Acid Phosphatase from potato
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
lyophilized powder
Quality Level
specific activity
≥3.0 units/mg solid
mol wt
69 kDa
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
O(CC(O)C)CC#C
InChI
1S/C6H10O2/c1-3-4-8-5-6(2)7/h1,6-7H,4-5H2,2H3
InChI key
GZCWLCBFPRFLKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Acid phosphatase from potato is a phosphomonoesterase, which can appear in multiple molecular forms of similar molecular mass but with different isoelectric points.
Application
Acid phosphatase from potato has been used in a study to assess the potential allergenicity of novel gene products. It has also been used in a study to remove eight phosphate groups from casein at a pH of 7.0.
The activity of potato acid phosphatase in various surfactant medias was examined. Bis(2- ethylhexyl)sodium sulfosuccinate, Brij 35, and SDS at 3mM inhibited phosphatase activity while the surfactant cetyltrimethylammonium bromide enhanced activity.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Acid phosphatases (APase) are a family of enzymes that non-specifically catalyze the hydrolysis of monoesters and anhydrides of phosphoric acid to produce inorganic phosphate at an optimum pH of 4 to 7.
Unit Definition
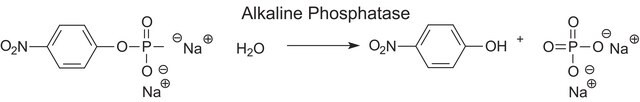
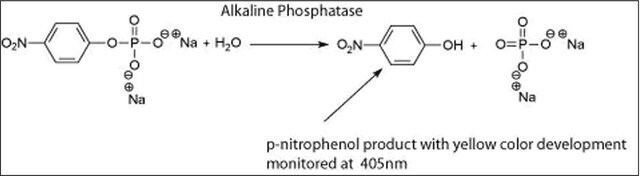
One unit will hydrolyze 1.0 μmole of p-nitrophenyl phosphate per min at pH 4.8 at 37 °C.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
J Lalitha et al.
Biochemistry and molecular biology international, 41(4), 797-803 (1997-04-01)
The effect of three different classes of surfactants viz., anionic, cationic and neutral on catalytic activity of potato acid phosphatase (AcPase) was studied. Anionic surfactants bis(2-ethylhexyl) sodium sulfosuccinate (AOT) and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) inhibited AcPase activity completely at 3
S I Tu et al.
Plant physiology, 88(1), 61-68 (1988-09-01)
Primary cell walls, free from cytoplasmic contamination were prepared from corn (Zea mays L.) roots and potato (Solanum tuberosum) tubers. After EDTA treatment, the bound acid phosphatase activities were measured in the presence of various multivalent cations. Under the conditions
P P Waymack et al.
Archives of biochemistry and biophysics, 288(2), 621-633 (1991-08-01)
An acid phosphatase (orthophosphoric monoester phosphohydrolase, acid optimum; EC 3.1.3.2) isoenzyme from wheat germ was purified 7000-fold to homogeneity. The effect of wheat germ sources and their relationship to the isoenzyme content and purification behavior of acid phosphatases was investigated.
Sishuo Cao et al.
Regulatory toxicology and pharmacology : RTP, 63(2), 181-187 (2012-04-17)
With the development of genetically modified crops, there has been a growing interest in available approaches to assess the potential allergenicity of novel gene products. We were not sure whether Cry1C could induce allergy. We examined the protein with three
J B Vincent et al.
Trends in biochemical sciences, 17(3), 105-110 (1992-03-01)
Formation of phosphate esters by kinases has long been recognized as an important process in biochemistry, but the reverse reaction, hydrolysis of phosphate esters by phosphatases, has attracted less attention. Recent work suggests that phosphatases are as important as kinases
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service