F6755
Fibrinogen from rat plasma
60-80% protein (≥60% of protein is clottable)
Synonym(s):
Factor I
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
rat plasma
Quality Level
form
powder
quality
60-80% protein (≥60% of protein is clottable)
mol wt
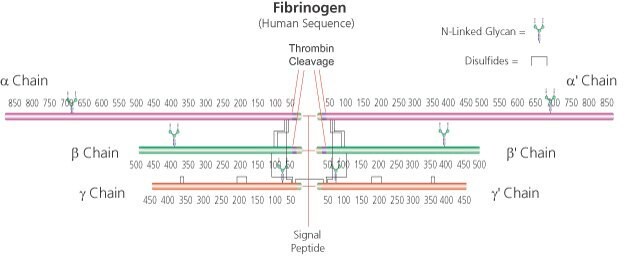
α-chain 63.5 kDa
β-chain 56 kDa
γ chain 47 kDa (about 4% carbohydrate content)
soluble dimer 340 kDa
concentration
60-80% (biuret)
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
immunoblotting: suitable
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
rat ... Fga(361969) , Fgb(24366) , Fgg(24367)
Application
Fibrinogen from rat plasma has been used:
- in the preparation of growth factor solutions
- to apply on discontinuous SDS-polyacrylamide gels for the detection of IgG (immunoglobulins) type antibodies by immunoblot analysis
- to mix with cell suspension to form a clot and retain the cells for avoiding its dispersion during transplantation
Fibrinogen has been used in studies of haemostatic therapy in surgical and massive trauma patients. These studies have shown that fibrinogen may prove to be more superior in stopping blood loss when compared to using fresh frozen plasma (FFP).
Biochem/physiol Actions
Acute phase protein that is part of the coagulation cascade of proteins.
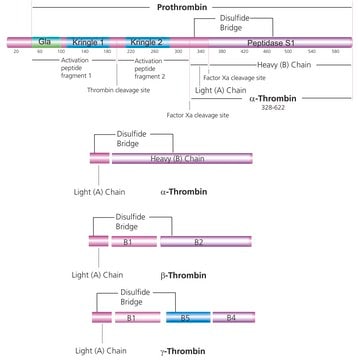
Fibrinogen is an acute phase protein that is part of the coagulation cascade of proteins. The end result of the cascade is the production of thrombin that converts fibrinogen to fibrin. Thrombin rapidly proteolyses fibrinogen, releasing fibrinopeptide A. The loss of this small peptide is not sufficient to make the resulting fibrin molecule insoluble, but it tends to form complexes with adjacent fibrin and fibrinogen molecules. Thrombin then cleaves a second peptide, fibrinopeptide B, from fibrin and the fibrin monomers formed then polymerize spontaneously to form an insoluble gel. The polymerized fibrin is held together by noncovalent and electrostatic forces and stabilized by the transamidating enzyme, factor XIIIa, that is produced by the action of thrombin on factor XIII. The insoluble fibrin aggregates (clots) and aggregated platelets then block the damaged blood vessel and prevent further bleeding. The amount of fibrinogen in the plasma can serve as a nonspecific indicator of whether or not an inflammatory process is present in the body. Fibrinogen from any mammalian source will be cleaved by thrombin from any mammalian source.
Quality
Contains ~12% sodium citrate and ~18% sodium chloride.
Analysis Note
Protein determined by biuret.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Cell Transplantation as a Method to Investigate Spinal Cord Regeneration in Regenerative and Nonregenerative Xenopus Stages
Mendez-Olivos EE and LarraIn J
Cold Spring Harbor Protocols (2018)
Optimization of trophic support for neural stem cell grafts in sites of spinal cord injury
Robinson J and Lu P
Experimental Neurology, 291, 87-97 (2017)
Salmon fibrin glue in rats: antibody studies
Laidmae I, et al.
Biologicals : Journal of the International Association of Biological Standardization, 40(1), 55-60 (2012)
C Fenger-Eriksen et al.
British journal of anaesthesia, 101(6), 769-773 (2008-09-27)
Patients experiencing massive haemorrhage are at high risk of developing coagulopathy through loss, consumption, and dilution of coagulation factors and platelets. It has been reported that plasma fibrinogen concentrations may reach a critical low level relatively early during bleeding, calling
Richard J Fish et al.
Blood, 123(14), 2278-2281 (2014-02-21)
Mutations in the human fibrinogen genes can lead to the absence of circulating fibrinogen and cause congenital afibrinogenemia. This rare bleeding disorder is associated with a variable phenotype, which may be influenced by environment and genotype. Here, we present a
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service