C9281
Cholesterol Esterase from Pseudomonas fluorescens
lyophilized powder, ≥10,000 units/g protein
Synonym(s):
CE, bile salt-stimulated lipase, cholesteryl ester hydrolase, pancreatic cholesterol esterase, Sterol-ester acylhydrolase
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
Pseudomonas fluorescens
Quality Level
Assay
10-30% (TCA-Biuret)
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
≥10,000 units/g protein
mol wt
~129 kDa
composition
Protein, ~20%
storage condition
under inert gas (argon)
technique(s)
cell based assay: suitable
color
tan to brown
pH
7-9
solubility
0.4 M potassium phosphate, pH 7.0: soluble 1.0 mg/mL
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
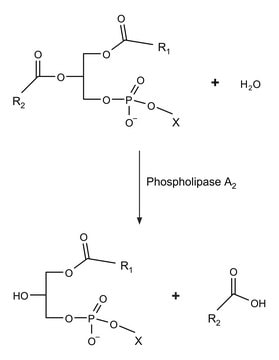
Cholesterol Esterase (CE) is a glycoprotein that can be isolated from fungal species such as Candida cylindracea and Pseudomonas fluorescens. It is classified as a member of the lipase/esterase family and functions as a homo-dimeric protein. CE is produced in the pancreas and is released in an active form upon stimulation by Cholecystokinin (CCK).
Application
- in cholesterol esterase assay to quantify total cholesterol from human blood serum samples
- a study to investigate the nondenaturing protein electro transfer of the esterase activity of lipolytic preparations
- an optimization study of components in enzymatic cholesterol reagents containing cholesterol oxidase
- for the modification of human plasma low-density-lipoprotein (LDL) to induce endothelial cell (EC) dysfunction and monocyte (MC) adhesion in the branched tissue-engineered blood vessels (TEBVs)
- to hydrolyze native cholesterol ester (CE) during filipin staining for detection of CE within the retinal frozen sections
Biochem/physiol Actions
Other Notes
Unit Definition
Analysis Note
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service