C1617
C Reactive Protein human
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, liquid
Synonym(s):
CRP
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
General description
C-reactive protein (CRP), a homopentameric acute-phase inflammatory protein, is produced mainly in liver hepatocytes. This highly conserved plasma protein is also produced by smooth muscle cells, macrophages, endothelial cells, lymphocytes, and adipocytes. It belongs to the pentraxin family.
Application
C Reactive Protein human has been used:
- as a component in differentiation medium to study the effects of C-reactive protein (CRP) on the size of myotubes and myotube mixed protein synthesis (MPS)
- to study the influence of serum CRP level from elderly on endothelial cell proliferation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC)
- to study the roles and connections of nicotine, monocytic interleukin 6 (IL-6), α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7-nAChR), and CRP in the development of coronary artery spasm (CAS)
Biochem/physiol Actions
C-reactive protein (CRP) plays a key role in the complement pathway, apoptosis, phagocytosis, nitric oxide (NO) release, and the production of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α. It participates in the uptake of low-density lipoprotein in macrophages. CRP levels are elevated in people suffering from appendicitis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, and meningitis. It plays a vital role in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular disease. Hence it is used as a marker of infection and cardiovascular events.
C-reactive protein (CRP) is a protein that could precipitate the C-polysaccharide of pneumococcal cell walls. CRP is widely used as a clinical marker of the state of inflammation, since its production by hepatocytes increases during the acute phase of the inflammatory response.
Analysis Note
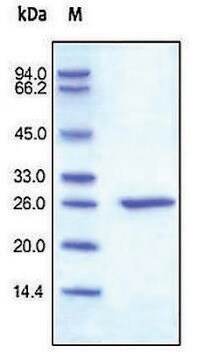
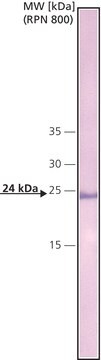
A highly purified protein and made by a fermentation process using genetically modified E. coli.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
nwg
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Adrian Hosford-Donovan et al.
Maturitas, 89, 52-57 (2016-05-18)
It is hypothesized that chronic systemic inflammation contributes to the age-related decline in cardiovascular function. The aim of the present study was to combine an assessment of the relationship between the serum level of C-reactive protein (CRP) and systolic and
Ajay Kumar Yagati et al.
Bioelectrochemistry (Amsterdam, Netherlands), 128, 165-174 (2019-04-21)
Most clinical tests for biomarker detection require the support of a laboratory, and the results are usually slow, less sensitive, and lack the possibility for Point-of-Care (PoC) testing. Further, with the increasing demand for sensitive, portable, rapid, and low-cost devices
Britta Wåhlin-Larsson et al.
Cellular physiology and biochemistry : international journal of experimental cellular physiology, biochemistry, and pharmacology, 44(1), 267-278 (2017-11-14)
Mechanisms underlying the relationship between systemic inflammation and age-related decline in muscle mass are poorly defined. The purpose of this work was to investigate the relationship between the systemic inflammatory marker CRP and muscle mass in elderly and to identify
Ioannis N Katis et al.
Biosensors & bioelectronics, 113, 95-100 (2018-05-09)
We report on the use of a laser-direct write (LDW) technique that allows the fabrication of lateral flow devices with enhanced sensitivity and limit of detection. This manufacturing technique comprises the dispensing of a liquid photopolymer at specific regions of
Yen-Kuang Lin et al.
Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity, 2022, 9964689-9964689 (2022-02-01)
Apolipoprotein (a)/lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)), a major carrier of oxidized phospholipids, and α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7-nAChR) may play an important role in the development of coronary artery spasm (CAS). In CAS, the association between Lp(a) and the α7-nAChR-modulated inflammatory macrophage polarization and
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service