900607
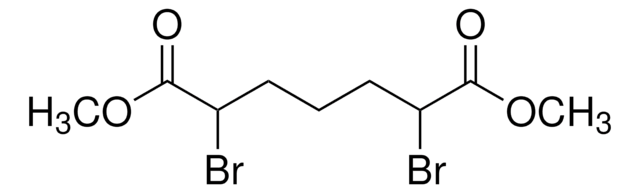
2,5-Dibromohexanediamide
≥95%
Synonym(s):
2,5-Dibromoadipamide, DBHDA
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C6H10Br2N2O2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
301.96
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥95%
form
solid
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
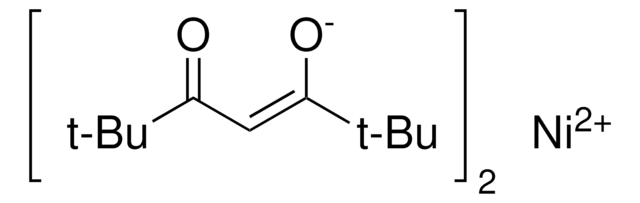
BrC(CCC(Br)C(=O)N)C(=O)N
InChI
1S/C6H10Br2N2O2/c7-3(5(9)11)1-2-4(8)6(10)12/h3-4H,1-2H2,(H2,9,11)(H2,10,12)
InChI key
PLSXNAQEJOGNKQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Application
This compound has been shown to be a useful reagent for the conversion of cysteine to dehydroalanine (DHA) in peptides or proteins. This enables chemical mutagenesis in which DHA can be efficiently reacted with iodide building blocks to add various natural and unnatural side chains on proteins. It was also shown that other modifications could be added through DHA such as phosphorylation, methylation, and glycosylation. In other research it was shown that DHA can be used to make ubiquitin conjugates that have a bond that mimics the native isopeptide bond.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Posttranslational mutagenesis: A chemical strategy for exploring protein side-chain diversity.
Wright TH, et al.
Science, 4(354), 6312-6312 (2016)
Methods for converting cysteine to dehydroalanine on peptides and proteins.
Chalker JM, et al.
Chemical Science, 2, 1666-1676 (2011)
Protein ubiquitination via dehydroalanine: development and insights into the diastereoselective 1,4-addition step.
Meledin R, et al.
Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 14(21), 4817-4823 (2016)
Philip R Lindstedt et al.
Cell chemical biology, 28(1), 70-77 (2020-11-21)
Great advances have been made over the last four decades in therapeutic and diagnostic applications of antibodies. The activity maturation of antibody candidates, however, remains a significant challenge. To address this problem, we present a method that enables the systematic
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service