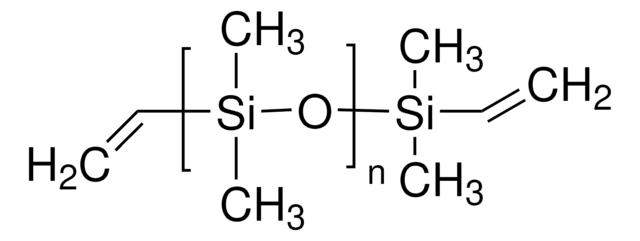805998
SYLGARD® 170 silicone elastomer
10 cc dual syringe with the static mixer
Synonym(s):
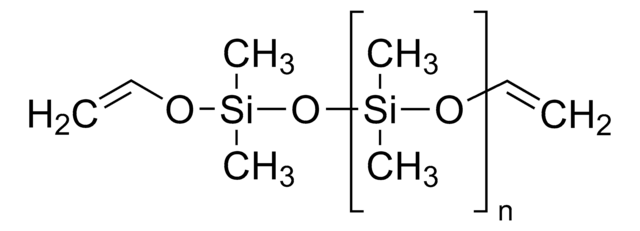
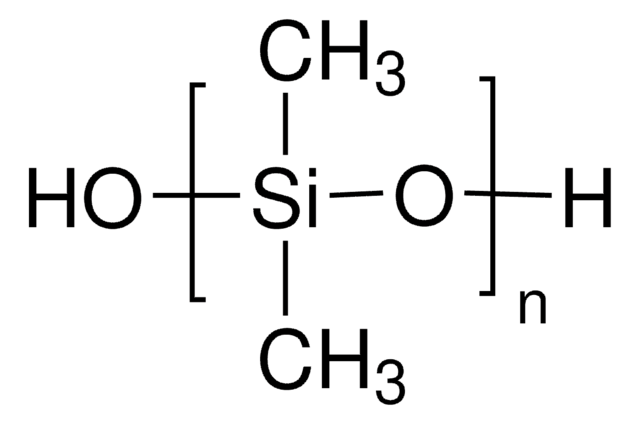
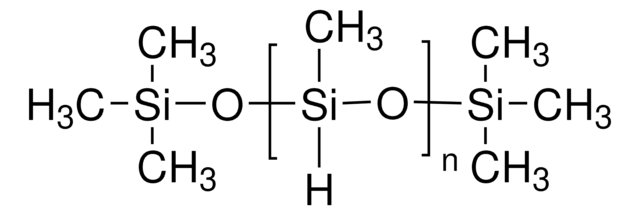
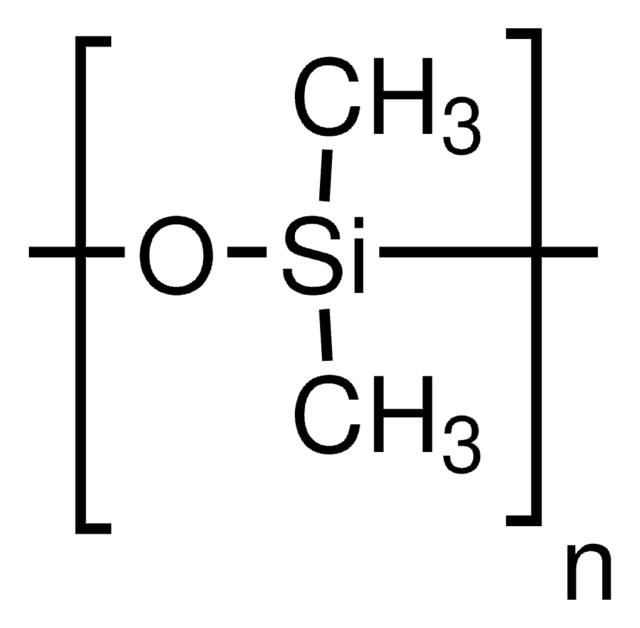
Curing agent, PDMS, Polydimethylsiloxane, Silicone, Silicone rubber
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
description
Form: Black liquid (part A), off-white liquid (part B)
Viscosity: 3160 cPs (part A), 1110 cPs (part B)
form
liquid
Related Categories
General description
- Two-part: 1:1 mixing ratio (pre-weighed).
- Low viscosity.
- Room temperature or heat accelerated cure.
- Rapid, versatile cure processing controlled by temperature.
- Moderate thermal conductivity.
- Enhanced flow and fill in narrow spaces and around complex geometries.
- Provides stress relief in applications where hard, rigid encapsulants can cause damage during thermal cycling.
- It can be considered for uses requiring added flame resistance and Mil Spec applications.
How to use:
Mixing: SYLGARD® 170 Silicone Elastomer is supplied in a dual syringe applicator with the static mixer consisting of Part A and Part B. The two components pre-weighed with 1:1 mixing ratio in the syringe applicator should be thoroughly mixed until the mixture has a uniform color. Vacuum de-airing is recommended. A residual pressure of 10-20 mmHg applied for 5-10 minutes will sufficiently de-air the material.
Curing: SYLGARD® 170 Silicone Elastomer should be cured using one of the following recommended schedules:
- 24 hours at 25°C or
- 25 minutes at 70°C or
- 10 minutes at 100°C.
Large components and assemblies may require longer times in order to reach the curing temperature.
Certain chemicals, curing agents and plasticizers can inhibit cure. These include:
- Organo-tin compounds.
- Silicone rubber containing organo-tin catalysts.
- Sulfur, polysulphides, polysulphones and other sulphur containing materials.
- Amines, urethanes, amides and azides.
For most uses, silicone encapsulants should be operational over a temperature range of -45 to 200°C (-49 to 392°F) for long periods of time.
Application
Potential applications:
- Power supplies
- Connectors
- Sensors
- Industrial controls
- Transformers
- Amplifiers
- High voltage resistor packs
- Relays
Preparation Note
PROCESSING/CURING - Thoroughly mixed Dow silicone encapsulants may be poured/dispensed directly into the container in which it is to be cured. Care should be taken to minimize air entrapment. When practical, pouring/dispensing should be done under vacuum, particularly if the component being potted or encapsulated has many small voids. If this technique cannot be used, the unit should be evacuated after the silicone encapsulant has been poured/ dispensed. Dow silicone encapsulants may be either room temperature (25°C/77°F) or heat cured. Room temperature cure encapsulants may also be heat accelerated for faster cure. Ideal cure conditions for each product are given in the product selection table.
POT LIFE AND CURE RATE - Cure reaction begins with the mixing process. Initially, cure is evidenced by a gradual increase in viscosity, followed by gelation and conversion to a solid elastomer. Pot life is defined as the time required for viscosity to double after Parts A and B (base and curing agent) are mixed and is highly temperature and application dependent.
USEFUL TEMPERATURE RANGES - For most uses, silicone encapsulants should be operational over a temperature range of -45 to 200°C (-49 to 392°F) for long periods of time. However, at both the low- and high temperature ends of the spectrum, behavior of the materials and performance in particular applications can become more complex and require additional considerations and should be adequately tested for the particular end use environment. For low-temperature performance, thermal cycling to conditions such as -55°C (-67°F) may be possible, but performance should be verified for your parts or assemblies. Factors that may influence performance are configuration and stress sensitivity of components, cooling rates and hold times, and prior temperature history. At the high temperature end, the durability of the cured silicone elastomer is time and temperature dependent. As expected, the higher the temperature, the shorter the time the material will remain useable.
COMPATIBILITY - Certain materials, chemicals, curing agents and plasticizers can inhibit the cure of addition cure gels. Most notable of these include: organotin and other organometallic compounds, silicone rubber containing organotin catalyst, sulfur, polysulfides, polysulfones or other sulfur containing materials, unsaturated hydrocarbon plasticizers, and some solder flux residues. If a substrate or material is questionable with respect to potentially causing inhibition of cure, it is recommended that a small scale compatibility test be run to ascertain suitability in a given application. The presence of liquid or uncured product at the interface between the questionable substrate and the cured gel indicates incompatibility and inhibition of cure.
Legal Information
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Advances in the area of soft optoelectronics, with a focus on the development of organic optoelectronic devices on shape memory polymers (SMP) is discussed.
Related Content
We offer PDMS surface modification kit which allows for durable hydrophilization of various polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) surfaces.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service