25190
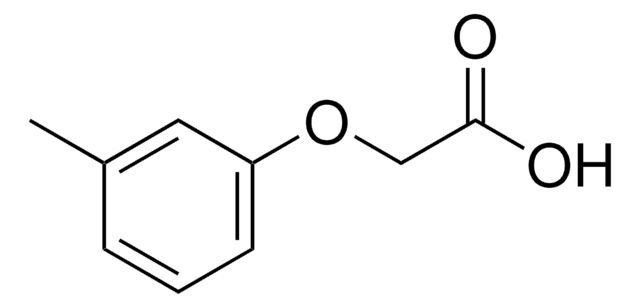
4-Chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetic acid
technical, ≥95.0% (T)
Synonym(s):
4-Chloro-o-tolyloxyacetic acid, MCPA
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
ClC6H3(CH3)OCH2CO2H
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
200.62
Beilstein:
2051752
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
grade
technical
Assay
≥95.0% (T)
form
solid
mp
114-118 °C (lit.)
solubility
water: insoluble(lit.)
functional group
carboxylic acid
SMILES string
Cc1cc(Cl)ccc1OCC(O)=O
InChI
1S/C9H9ClO3/c1-6-4-7(10)2-3-8(6)13-5-9(11)12/h2-4H,5H2,1H3,(H,11,12)
InChI key
WHKUVVPPKQRRBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
4-Chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetic acid (MPCA) is a herbicide. Various MCPA-mineralising bacterial combinations has been tested using a high-throughput microplate radiorespirometric mineralisation assay. Degradation mechanisms of OH and MCPA including molecular form and anionic form have been studied. Rapid and sensitive LC-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry method has been developed for the quantitation of MCPA in water and soil samples.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Urse S Krüger et al.
Pest management science, 71(2), 257-265 (2014-04-17)
The herbicide 4-chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetic acid (MCPA) is found frequently in Danish groundwater in concentrations exceeding the EU threshold limit of 0.1 µg L(-1) . Groundwater is used for drinking water, and one potential remediation strategy is bioaugmentation using inoculation of sand filters at
Xiaohua Ren et al.
Chemosphere, 88(1), 39-48 (2012-03-27)
The initial degradation mechanisms of ⁱOH and 4-chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetic acid (MCPA) including molecular form and anionic form are studied at the MPWB1K/6-311+G(3df, 2p)//MPWB1K/6-31+G(d, p) level. Possible reaction pathways of H-atom abstraction and ⁱOH addition are considered in detail. By result comparison
Erkin Gözdereliler et al.
Applied and environmental microbiology, 79(1), 367-375 (2012-11-06)
Two 4-chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetic acid (MCPA)-degrading enrichment cultures selected from an aquifer on low (0.1 mg liter(-1)) or high (25 mg liter(-1)) MCPA concentrations were compared in terms of metabolic activity, community composition, population growth, and single cell physiology. Different community compositions
G G Bond et al.
British journal of industrial medicine, 50(4), 340-348 (1993-04-01)
For the purpose of assessing the human carcinogenic potential of the chlorophenoxy herbicides MCPA, MCPP, and 2,4-DP, the relevant epidemiological and toxicological evidence is reviewed. These compounds have not produced tumours in animal studies conducted under current test guidelines, giving
Edgar Hiller et al.
Chemosphere, 87(5), 437-444 (2011-12-31)
Herbicide leaching through soil into groundwater greatly depends upon sorption-desorption and degradation phenomena. Batch adsorption, desorption and degradation experiments were performed with acidic herbicide MCPA and three soil types collected from their respective soil horizons. MCPA was found to be
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service