E6908
pFLAG-CMV™-5.1 Expression Vector
shuttle vector for intracellular transient expression of C-terminal FLAG
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
Recommended Products
tag
FLAG® tagged
grade
for molecular biology
form
buffered aqueous solution
Peptide tag location
C-terminal
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
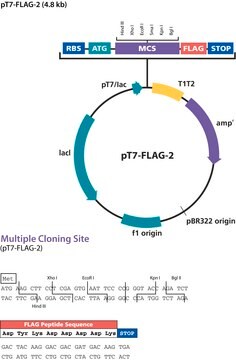
The pFLAG-CMV™-5.1 Expression Vector is a 4.7 kb derivative of the pCMV5 transient expression vector, used for establishing transient intracellular expression of C-terminal FLAG® fusion proteins in mammalian cells.
pFLAG-CMV-5.1 is a shuttle vector for E. coli and mammalian cells. Efficiency of replication and genomic integration is optimal when using an SV40 T antigenexpressing host.
The pFLAG-CMV-5b-BAP Control Plasmid is a 6.0 kb derivative of the pCMV5 transient expression vector for intracellular expression of C-terminal FLAG bacterial alkaline phosphatase fusion protein in mammalian cells.
Vector Maps and Sequences
pFLAG-CMV-5.1 is a shuttle vector for E. coli and mammalian cells. Efficiency of replication and genomic integration is optimal when using an SV40 T antigenexpressing host.
The pFLAG-CMV-5b-BAP Control Plasmid is a 6.0 kb derivative of the pCMV5 transient expression vector for intracellular expression of C-terminal FLAG bacterial alkaline phosphatase fusion protein in mammalian cells.
Vector Maps and Sequences
Application
pFLAG-CMV™-5.1 Expression Vector is suitable for transient or stable expression and secretion of N-terminal FLAG®-tagged fusion proteins in mammalian cells.
Components
- pFLAG-CMV™-5.1 Expression Vector 20 μg (E7901) is supplied as 0.5 mg/ml in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) with 1 mM EDTA.
- pFLAG-CMV™-5b-BAP Control Plasmid 20 μg (P5225) is supplied as 0.5 mg/ml in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) with 1 mM EDTA.
Principle
The promoter-regulatory region of the human cytomegalovirus drives transcription of FLAG®-fusion constructs. The multiple cloning region of the pFLAG-CMV™-5.1 vector is not preceded by a translational initiation signal. A translational start sequence must be included with the insert DNA. The multiple cloning region of the pFLAG-CMV-5.1 vector is compatible with other CMV vectors.
Legal Information
FLAG is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
pFLAG-CMV is a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Monica Red Brewer et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(38), E3595-E3604 (2013-09-11)
The initiation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) kinase activity proceeds via an asymmetric dimerization mechanism in which a "donor" tyrosine kinase domain (TKD) contacts an "acceptor" TKD, leading to its activation. In the context of a ligand-induced dimer, identical
Ya-Fang Chiu et al.
Journal of virology, 86(18), 9647-9655 (2012-06-29)
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) BBLF1 shares 13 to 15% amino acid sequence identities with the herpes simplex virus 1 UL11 and cytomegalovirus UL99 tegument proteins, which are involved in the final envelopment during viral maturation. This study demonstrates that BBLF1 is
Vladimir Majerciak et al.
Journal of virology, 81(3), 1062-1071 (2006-11-17)
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) ORF57 regulates viral gene expression at the posttranscriptional level during viral lytic infection. To study its function in the context of the viral genome, we disrupted KSHV ORF57 in the KSHV genome by transposon-based mutagenesis. The
Kristina W Thiel et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(49), 19238-19243 (2007-11-29)
Structural studies of the extracellular and tyrosine kinase domains of the epidermal growth factor receptor (ErbB-1) provide considerable insight into facets of the receptor activation mechanism, but the contributions of other regions of ErbB-1 have not been ascertained. This study
Svetlana Gorokhova et al.
Human molecular genetics, 16(20), 2394-2410 (2007-07-04)
We characterized a family consisting of four mammalian proteins of unknown function (NKAIN1, 2, 3 and 4) and a single Drosophila ortholog dNKAIN. Aside from highly conserved transmembrane domains, NKAIN proteins contain no characterized functional domains. Striking amino acid conservation
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service