SML0982
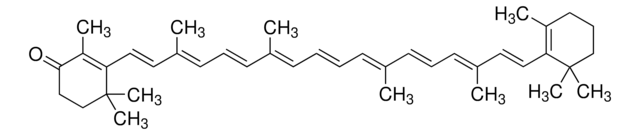
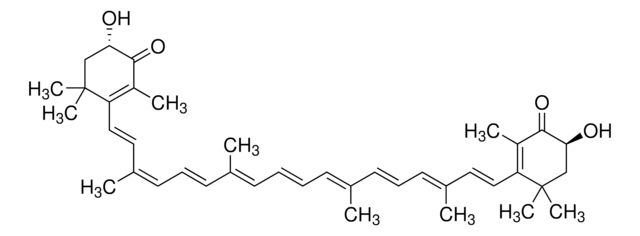
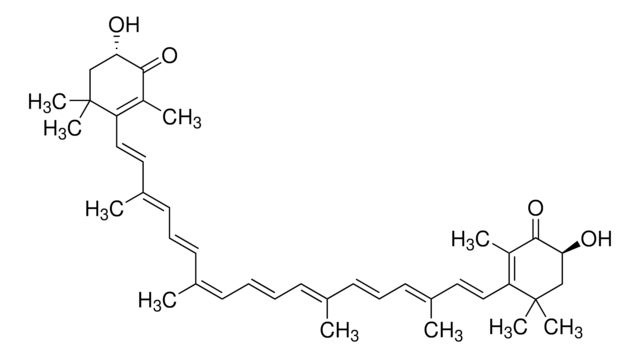
Astaxanthin
from Blakeslea trispora, ≥97% (HPLC), powder, PPARγ
Synonym(s):
3,3′-Dihydroxy-β-carotene-4,4′-dione, trans-Astaxanthin
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
Astaxanthin, ≥97% (HPLC), from Blakeslea trispora
biological source
Blakeslea trispora
Quality Level
Assay
≥97% (HPLC)
form
powder
storage condition
desiccated
protect from light
color
, pink to very dark purple
solubility
DMSO: 1 mg/mL (warmed)
storage temp.
−20°C
InChI
1S/C40H52O4/c1-27(17-13-19-29(3)21-23-33-31(5)37(43)35(41)25-39(33,7)8)15-11-12-16-28(2)18-14-20-30(4)22-24-34-32(6)38(44)36(42)26-40(34,9)10/h11-24,35-36,41-42H,25-26H2,1-10H3/b12-11+,17-13+,18-14+,23-21+,24-22+,27-15+,28-16+,29-19+,30-20+/t35-,36-/m0/s1
InChI key
MQZIGYBFDRPAKN-UWFIBFSHSA-N
General description
Application
- as an antioxidant to study its effect on Brachionus manjavacas (Rotifera) population growth
- to study its effects on the treatment of diabetic retinopathy.
- to investigate its role in restoring the expression of Nrf2 (nuclear factor erythroid 2 p45-related factor 2) and glutathione S-transferase P1 (GSTP1) through epigenetic modification in human prostate LNCaP cells.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Other Notes
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Protocols
Protocol for HPLC Analysis of Carotene Compounds on Ascentis® RP-Amide
Related Content
Separation of Astaxanthin; Xanthophyll
DISCOVER Bioactive Small Molecules for Nitric Oxide & Cell Stress Research
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service



![1,8-Diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene 98%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/120/564/5b373e23-1624-489c-8efb-692de0f96ffb/640/5b373e23-1624-489c-8efb-692de0f96ffb.png)