H3884
Hyaluronidase from bovine testes
Type IV-S, lyophilized powder (essentially salt-free), 750-3000 units/mg solid
Synonym(s):
Hyaluronate 4-glycanohydrolase, Hyaluronoglucosaminidase
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
bovine testis
Quality Level
conjugate
conjugate (Glucosaminoglycan)
type
Type IV-S
form
lyophilized powder (essentially salt-free)
specific activity
750-3000 units/mg solid
mol wt
~55 kDa (four subunits of 14 kDa each)
application(s)
diagnostic assay manufacturing
relevant disease(s)
cancer
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
cow ... HYAL1(515397) , HYAL2(281838)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Biochem/physiol Actions
Unit Definition
Other Notes
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Hepatocytes are epithelial cells found in the liver. They perform important functions, such as helping to detoxify blood, and to synthesize transport proteins, such as lipoprotein, albumin and transferrin. Primary and secondary cultures of hepatocytes are useful for studying the mechanisms of liver regeneration and differentiation.
A key resource feature at our Enzyme Explorer section of biochemicals is "Enzymes for Carbohydrate Analysis and Digestion." Offering kits, reagents, analysis, lists of enzymes related to PTM and carbohydrate metabolism.
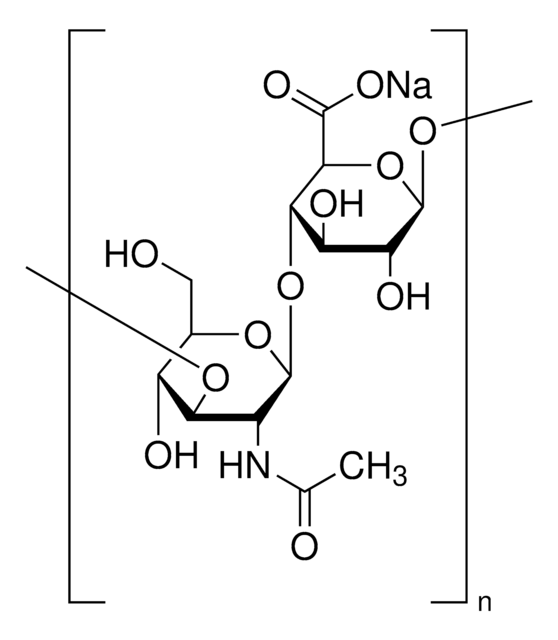
Glycosaminoglycans are large linear polysaccharides constructed of repeating disaccharide units.
Protocols
This procedure may be used for Hyaluronidase products.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service