C3860
Cytochrome P450 human
1B1 Isozyme Microsomes, with P450 Reductase, recombinant, expressed in baculovirus infected insect cells (BTI-TN-5B1-4)
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
human
Quality Level
recombinant
expressed in baculovirus infected insect cells (BTI-TN-5B1-4)
form
solution
mol wt
45-60 kDa
packaging
vial of 0.5 nmol
UniProt accession no.
application(s)
cell analysis
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−70°C
Gene Information
human ... CYP1B1(1545)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Biochem/physiol Actions
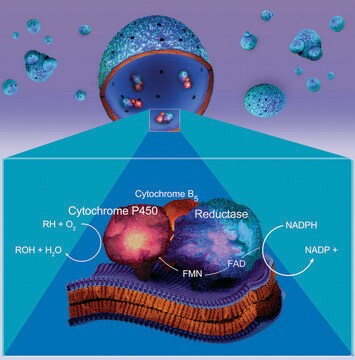
Cytochrome P450 is a heterogeneous family of isozymes whose primary function is to oxidize small molecules, both as a function of intermediary metabolism (e.g., fatty acids) and to detoxify exogenous compounds (drugs or toxins). Some isoforms have narrow substrate specificity, while others are promiscuous.
Unit Definition
One unit will reduce 1 nanomole of cytochrome C per minute at pH 7.4 at 37 deg C.
Physical form
Solution in 100 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4.
Preparation Note
Microsomes containing human CYP1B1 and recombinant human NADPH-P450 reductase.
Analysis Note
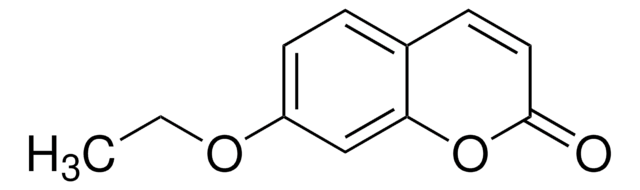
Tested for the ability to catalyze the 7-deethylation of ethoxyresorufin.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
D P Bofinger et al.
Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology, 62(2), 299-314 (2001-07-14)
Endometriosis is a debilitating disease estimated to affect 10% of reproductive-age women and characterized by the growth of endometrial tissue outside of the uterus. The present study characterizes a human endometrial explant culture model for studying the direct effects of
Hua Liu et al.
Science advances, 6(1), eaay3566-eaay3566 (2020-01-09)
In this study, we investigated the roles of Epac1 in pathological angiogenesis and its potential as a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of vasoproliferative diseases. Genetic deletion of Epac1 ameliorated pathological angiogenesis in mouse models of oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR)
Xiangrong Zhang et al.
PloS one, 9(4), e94962-e94962 (2014-04-17)
The present study characterized in vitro metabolites of 20(R)-25-methoxyl-dammarane-3β, 12β, 20-triol (20(R)-25-OCH3-PPD) in mouse, rat, dog, monkey and human liver microsomes. 20(R)-25-OCH3-PPD was incubated with liver microsomes in the presence of NADPH. The reaction mixtures and the metabolites were identified
Mirza Bojić et al.
Drug metabolism and disposition: the biological fate of chemicals, 42(9), 1438-1446 (2014-07-06)
Cilengitide is a stable cyclic pentapeptide containing an Arg-Gly-Asp motif responsible for selective binding to αVβ3 and αVβ5 integrins. The candidate drug showed unexpected inhibition of cytochrome P450 (P450) 3A4 at high concentrations, that is, a 15-mM concentration caused attenuation
Dongju Lin et al.
Drug metabolism and disposition: the biological fate of chemicals, 42(10), 1727-1736 (2014-07-16)
Diosbulbin B (DIOB), a furan-containing diterpenoid lactone, is the most abundant component of Dioscorea bulbifera L. (DB), a traditional Chinese medicine herb. Administration of purified DIOB or DB extracts has been reported to cause liver injury in animals. The mechanisms
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service