A8200
Aminopeptidase from Aeromonas proteolytica
lyophilized powder, 50-150 units/mg protein
Synonym(s):
AAP, Aminopeptidase from Vibrio proteolyticus, bacterial leucyl aminopeptidase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
CAS Number:
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.54
Recommended Products
grade
Proteomics Grade
Quality Level
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
50-150 units/mg protein
mol wt
29.5 kDa
composition
Protein, ~40% biuret
solubility
H2O: soluble 0.9-1.1 mg/mL, clear, colorless
foreign activity
endopeptidase, essentially free
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
A zinc-containing enzyme.
Specificity
Catalyzes the release of an N-terminal amino acid, preferentially leucine, but not glutamic or aspartic acids.
Application
Aminopeptidases are a family of widely distributed proteases, which may be used to study many significant biological processes such as protein maturation, hormone production, and peptide digestion. The enzyme has been used to measure the kinetic rate constant for the binding of bestatin, a general protease inhibitor, to aminopeptidase.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Aminopeptidase from Aeromonas proteolytica is a metalloenzyme, which contains 2 atoms of Zn2+ in a single polypeptide with an approximate molecular weight of 29.5 kDa as determined by sedimentation. This enzyme has a high degree of stability, being stable even at temperatures of 70 °C for several hours. Partial inactivation occurs in 8 M urea. Maximum stability and activity are between pH 8.0-8.5. Aminopeptidase from Aeromonas proteolytica can function as an esterase.
Aminopeptidase from Aeromonas proteolytica is involved in protein maturation, hormone production and peptide digestion.
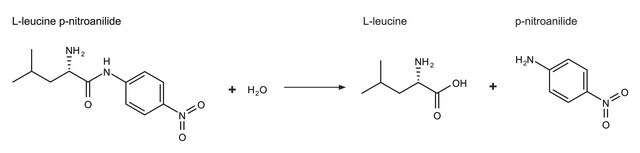
Unit Definition
One unit will hydrolyze 1.0 μmole of L-leucine p-nitroanilide to L-leucine and p-nitroaniline per min at pH 8.0 at 25 °C.
Physical form
Lyophilized powder containing tricine buffer, pH 8.0, zinc chloride and stabilizer.
Preparation Note
Dissolves in water at 0.9-1.1 mg/mL concentration to form a clear, colorless solution.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
James Kahn et al.
Biochemistry and molecular biology education : a bimonthly publication of the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 38(4), 238-241 (2011-05-14)
We have recently designed a biochemistry laboratory experiment for the purpose of providing students an advanced experience with enzyme kinetics and the kinetics of binding. Bestatin, a well-known and commercially available general protease inhibitor, is a slow-binding inhibitor of aminopeptidase
S Nirasawa et al.
The Biochemical journal, 341 ( Pt 1), 25-31 (1999-06-23)
An aminopeptidase from Aeromonas caviae T-64 was translated as a preproprotein consisting of three domains; a signal peptide (19 amino acid residues), an N-terminal propeptide (101 residues) and a mature region (273 residues). We demonstrated that a proteinase, which was
Krzysztof P Bzymek et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 279(30), 31018-31025 (2004-05-13)
Glutamate 151 has been proposed to act as the general acid/base during the peptide hydrolysis reaction catalyzed by the co-catalytic metallohydrolase from Aeromonas proteolytica (AAP). However, to date, no direct evidence has been reported for the role of Glu-151 during
Kiet T Nguyen et al.
Methods in molecular medicine, 142, 117-130 (2008-04-26)
The emergence of bacterial pathogens resistant to current antibiotics has caused an urgent demand for new treatments. Peptide deformylase (PDF) has become an exciting target for designing novel antibiotics. To facilitate the screening of PDF inhibitors, three robust, coupled assays
K M Huntington et al.
Biochemistry, 38(47), 15587-15596 (1999-11-26)
Peptide-derived thiols of the general structure N-mercaptoacyl-leucyl-p-nitroanilide (1a-c) were synthesized and found to be potent, slow-binding inhibitors of the aminopeptidase from Aeromonas proteolytica (AAP). The overall potencies (K(I)) of these inhibitors against AAP range from 2.5 to 57 nM exceeding
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service