EZHGIP
Human GIP ELISA Kit
measures and quantify total GIP levels in 20 μL serum, plasma or cell culture samples
Synonym(s):
Gastric inhibitory polypeptide, Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, Incretin hormone
About This Item
Recommended Products
product name
Human GIP (total) ELISA, This Human GIP (total) ELISA is used to measure & quantify GIP levels in Metabolism & Endocrine research.
Quality Level
species reactivity
human
packaging
kit of 1 × 96 wells
parameter
20 μL sample volume (4hr assay)
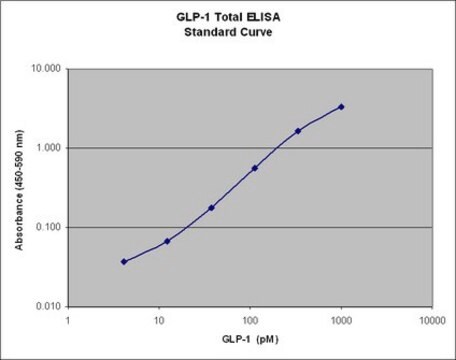
assay range
accuracy: 86.7%
linearity: 99.9%
sensitivity: 8.2 pg/mL
standard curve range: 8.2-2000 pg/mL
technique(s)
ELISA: suitable
input
sample type cell culture supernatant
sample type serum
sample type plasma (K2 EDTA)
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
application(s)
research use
detection method
colorimetric (450nm/590nm)
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
2-8°C
Gene Information
human ... GNAI2(2771)
General description
Application
Other Notes
Disclaimer
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Met. Corr. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service