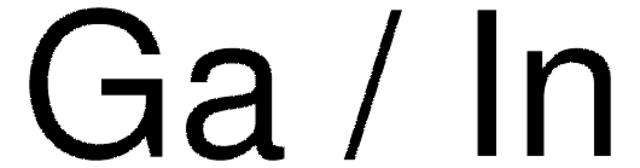357308
Indium
foil, thickness 0.1 mm, ≥99.995% trace metals basis
Synonym(s):
Indium element
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
In
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
114.82
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12141719
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
vapor pressure
<0.01 mmHg ( 25 °C)
Quality Level
Assay
≥99.995% trace metals basis
form
foil
resistivity
8.37 μΩ-cm
thickness
0.1 mm
mp
156.6 °C (lit.)
density
7.3 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
[In]
InChI
1S/In
InChI key
APFVFJFRJDLVQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Indium foil is widely used in nuclear facilities to capture thermal neutrons, because it shows a high cross section of neutron capture reaction. Hence, it may be used in dosemeters to measure exposure. Indium foils were studied for simultaneous monitoring neutron and photon intensities in a reactor core.
Application
Wetting behaviour of eutectic gallium-indium alloys on bare indium foil was investigated.
Quantity
1.8 g = 50 × 50 mm; 7.2 g = 100 × 100 mm
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
STOT RE 1 Inhalation
Target Organs
Lungs
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Rebecca K Kramer et al.
Langmuir : the ACS journal of surfaces and colloids, 30(2), 533-539 (2013-12-24)
Liquid-embedded elastomer electronics have recently attracted much attention as key elements of highly deformable and "soft" electromechanical systems. Many of these fluid-elastomer composites utilize liquid metal alloys because of their high conductivities and inherent compliance. Understanding how these alloys interface
Activation detection using indium foils for simultaneous monitoring neutron and photon intensities in a reactor core.
Chao JH and Chiang AC
Radiation Measurements, 45, 1024-1033 (2010)
Recalibration of Indium foil for personnel screening in criticality accidents
Takada C, et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 144(1-4), 575-579 (2010)
G W Shu et al.
Physical chemistry chemical physics : PCCP, 15(10), 3618-3622 (2013-02-06)
Nonradiative energy transfer from an InGaN quantum well to Ag nanoparticles is unambiguously demonstrated by the time-resolved photoluminescence. The distance dependence of the energy transfer rate is found to be proportional to 1/d(3), in good agreement with the prediction of
Juan Zhou et al.
Chemical communications (Cambridge, England), 49(22), 2237-2239 (2013-02-12)
A reduced graphene oxide (RGO)-ZnIn(2)S(4) nanosheet composite was successfully synthesized via an in situ controlled growth process. The as-obtained RGO-ZnIn(2)S(4) composite showed excellent visible light H(2) production activity in the absence of noble metal cocatalysts.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service