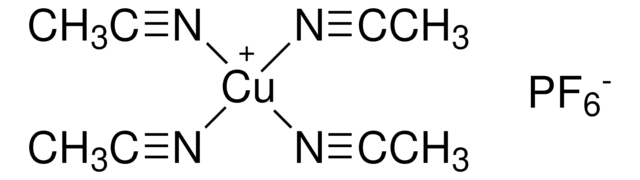
339768
Tetrakis(acetonitrile)palladium(II) tetrafluoroborate
Synonym(s):
NSC 307191, Palladium(II) tetrafluoroborate tetraacetonitrile complex
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
solid
Quality Level
reaction suitability
reaction type: Buchwald-Hartwig Cross Coupling Reaction
reaction type: Cross Couplings
reaction type: Heck Reaction
reaction type: Hiyama Coupling
reaction type: Negishi Coupling
reaction type: Sonogashira Coupling
reaction type: Stille Coupling
reaction type: Suzuki-Miyaura Coupling
reagent type: catalyst
core: palladium
reagent type: ligand
mp
230 °C (dec.) (lit.)
SMILES string
[Pd++].CC#N.CC#N.CC#N.CC#N.F[B-](F)(F)F.F[B-](F)(F)F
InChI
1S/4C2H3N.2BF4.Pd/c4*1-2-3;2*2-1(3,4)5;/h4*1H3;;;/q;;;;2*-1;+2
InChI key
YWMRPVUMBTVUEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
General description
Application
Reactant involved in:
- Reactions where it plays a role as the metal source due to weakly coordinated acetonitrile ligands
Precursor for:
- Synthesis of dendritic SCS-pincer palladium complexes
- Palladium complexes of click ligands
- Dipalladium catalysts for use in Heck cross-coupling, Suzuki cross-coupling, and aldehyde olefination
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
The Heck reaction is the palladium catalyzed cross-coupling reaction between alkenes and aryl or vinyl halides (or triflates) to afford substituted alkenes.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service