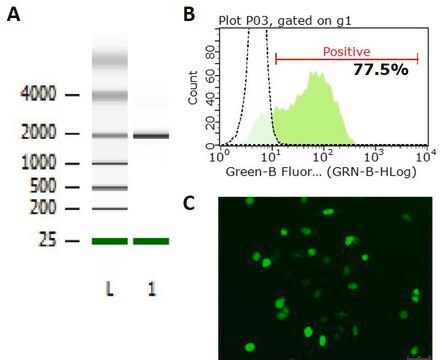
CSTZFN
CompoZr® Custom Zinc Finger Nuclease (ZFN)
ZFN plasmid and mRNA
Synonym(s):
Zinc Finger Nuclease
About This Item
Recommended Products
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
- Creation of gene knockouts in multiple cell lines
- Complete knockout of genes not amenable to RNAi
- Creation of knock-in cell lines with promoters, fusion tags or reporters integrated into endogenous genes
- Creation of cell lines that produce higher yields of proteins or antibodies
Features and Benefits
- Rapid design, assembly, and validation of a ZFN pair targeting your gene of interest
- Rapid and permanent disruption of, or integration into, any genomic loci
- Mutations made are permanent and heritable
- Works in a variety of mammalian somatic cell types
- Edits induced through a single transfection experiment
- Knockout or knock-in cell lines in as little as two months
- Single or biallelic edits occur in 1-20% of clone population
- No antibiotic selection required for screening
Components
- Best Performing ZFN Pair
- 10 Aliquots of Ready-to-Deliver ZFN Pair in mRNA form
- ZFN Pair in Plasmid Form
- Forward and Reverse Primers that allow for determination of rate of mutation and for screening of individual clones
- Positive Control DNA
- Used to determine a baseline cutting efficiency
Other Notes
Custom ZFN Service offering HERE
Legal Information
related product
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
Deciphering the genetics of neuroscience has always been challenging. Heterogeneous tissue microenvironments, complex genetic interactions and phenotypes, lack of model systems that accurately mimic the human brain transcriptome - not to mention the blood-brain barrier - make genetic perturbation analysis difficult in neural tissues.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service