A9918
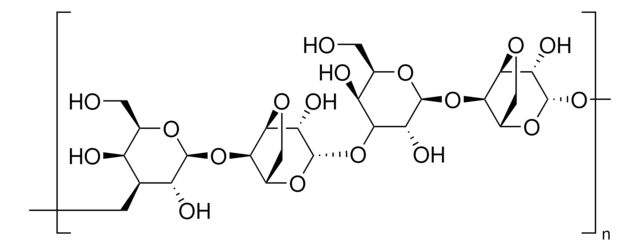
Agarose
Type II-A, Medium EEO
Synonym(s):
3,6-Anhydro-α-L-galacto-β-D-galactan, Agarose ME
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
algae (Gelidium)
Quality Level
type
Type II-A
form
powder
impurities
≤7% water
ash
≤0.5%
turbidity
≤40 NP (1.5% gel)
EEO
0.16-0.19
mp
86.5-89.5 °C
transition temp
gel point 36 °C ±1.5 °C (1.5% gel)
gel strength
≥1000 g/cm2 (1% gel)
anion traces
sulfate (SO42-): ≤0.25%
SMILES string
O1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@H]([C@H]1CO)O)O[C@@H]4O[C@@H]5[C@H]([C@@H](OC5)[C@@H]4O)O[C@@H]6O[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H]6O)O)O)CO)O)O[C@H]2[C@H]3OC[C@@H]2O[C@H]([C@H]3O)O
InChI
1S/C24H38O19/c25-1-5-9(27)11(29)12(30)22(38-5)41-17-8-4-36-20(17)15(33)24(40-8)43-18-10(28)6(2-26)39-23(14(18)32)42-16-7-3-35-19(16)13(31)21(34)37-7/h5-34H,1-4H2/t5-,6-,7+,8+,9+,10+,11+,12-,13+,14-,15+,16-,17-,18+,19+,20+,21-,22+,23+,24+/m1/s1
InChI key
MJQHZNBUODTQTK-WKGBVCLCSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
- Porous Agarose Layered Magnetic Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite for Virus RNA Monitoring in Wastewater.: This innovative study showcases the use of agarose in the creation of a nanocomposite material for environmental monitoring, specifically for tracking viral RNA in wastewater (He et al., 2024).
- Detection method for reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification of avian influenza virus subtypes H5, H7, and H9.: Demonstrates the application of agarose in the development of diagnostic tools for detecting and monitoring avian influenza, emphasizing its critical role in enhancing bioanalytical methods (Zhang et al., 2024).
- Evaluating Nanoparticles Penetration by a New Microfluidic Hydrogel-Based Approach.: This research utilizes agarose-based hydrogels in a microfluidic system to study nanoparticle penetration, offering insights into cellular interactions and nanoparticle dynamics that are essential for pharmaceutical development and nanotechnology (Goodarzi et al., 2024).
- Antibacterial efficacy of copper-based metal-organic frameworks against Escherichia coli and Lactobacillus.: Agarose has been used to perform agarose gel electrophoresis for the synthesis of copper-based metal-organic frameworks, enhancing the antimicrobial properties of these compounds. This application points to the expanding role of agarose in antimicrobial research, relevant for both clinical and agricultural settings (Elmehrath et al., 2024).
Analysis Note
Sulfate content - used as an indicator of purity, since sulfate is the major ionic group present.
Gel strength - the force that must be applied to a gel to cause it to fracture.
Gel point - the temperature at which an aqueous agarose solution forms a gel as it cools. Agarose solutions exhibit hysteresis in the liquid-to-gel transition - that is, their gel point is not the same as their melting temperature.
Electroendosmosis (EEO) - a movement of liquid through the gel. Anionic groups in an agarose gel are affixed to the matrix and cannot move, but dissociable counter cations can migrate toward the cathode in the matrix, giving rise to EEO. Since electrophoretic movement of biopolymers is usually toward the anode, EEO can disrupt separations because of internal convection.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service