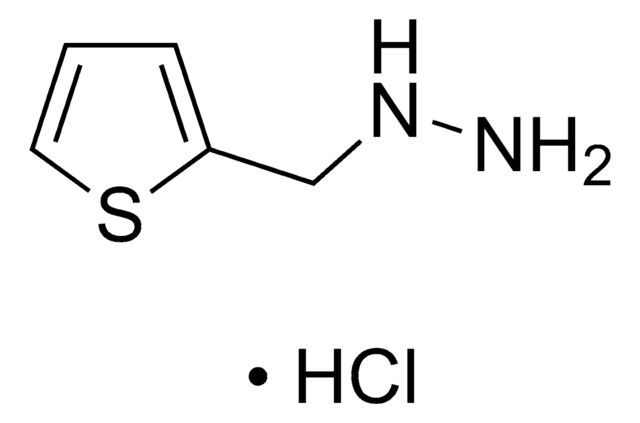
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C16H8N2O4
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
292.25
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
99%
form
solid
solubility
DMSO: soluble 2 mg/mL, clear, yellow to orange
functional group
nitro
SMILES string
[O-][N+](=O)c1cc([N+]([O-])=O)c2ccc3cccc4ccc1c2c34
InChI
1S/C16H8N2O4/c19-17(20)13-8-14(18(21)22)12-7-5-10-3-1-2-9-4-6-11(13)16(12)15(9)10/h1-8H
InChI key
KTNUVDBUEAQUON-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Related Categories
General description
The carcinogenecity of 1,3-dinitropyrene was studied in newborn female rats.
Application
1,3-Dinitropyrene has been used in:
- modification of the umu-assay (ISO 13829) to assess the cytotoxic potential of toxins
- in vitro synthesis of 1,N6-etheno-2′-deoxyadenosine and 1,N2-etheno-2′-deoxyguanosine
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
L B Tee et al.
Carcinogenesis, 9(10), 1869-1874 (1988-10-01)
Dinitropyrenes are mutagenic and carcinogenic environmental pollutants commonly found in diesel exhaust and airborne particulates. In the present study, the ability of rabbit lung to metabolize 1,8-dinitro[4,5,9,10-3H]pyrene by both oxygen-dependent and oxygen-independent pathways has been investigated. Using lung 9000 g
H Lee et al.
Mutation research, 324(1-2), 77-84 (1994-06-01)
The disposal of massive quantities of synthetic materials has become a very serious environmental problem around the world. When synthetic polymers are burnt or smolder in air, the combustion products are extremely complex, often consisting of several hundred compounds. In
A K Hajos et al.
Journal of biochemical toxicology, 6(4), 277-282 (1991-01-01)
The effect of highly purified rat liver cytosolic NAD(P)H-quinone oxidoreductase [EC 1.6.99.2] on the mutagenicity of 1,3- 1,6- and 1,8-dinitropyrene (DNP) was studied in the Ames Salmonella typhimurium mutagenicity assay. NAD(P)H-quinone oxidoreductase over the range of 0.02-0.8 micrograms/plate (38-1500) units
G W Winston et al.
Mutation research, 279(4), 289-298 (1992-06-16)
The effects of chronic ethanol feeding of rats on the ability of liver fractions to modulate the bacterial mutagenicity of three dinitropyrene isomers (1,3-, 1,6- and 1,8-DNP), which require bacterial enzymes but not an exogenous enzyme source for activation, were
C A Norman et al.
Carcinogenesis, 10(7), 1323-1327 (1989-07-01)
Formation of DNA adducts, following treatment of primary rabbit tracheal epithelial cells (RTEC) with 1,8-dinitropyrene (1,8-DNP) and its partially reduced derivative, 1-nitro-8-nitrosopyrene (1,8-NONO2), was examined using the 32P-post-labelling technique. Treatment of aerobic cells with 1,8-DNP or 1,8-NONO2 produced qualitatively similar
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service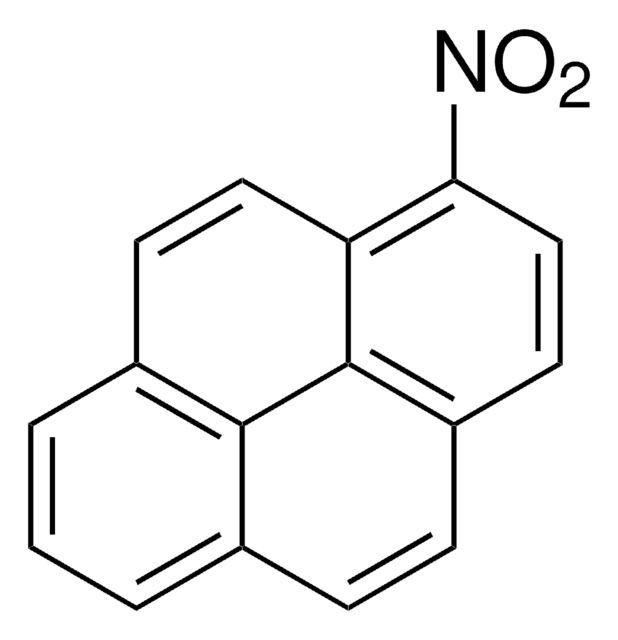
![1-(6-Methoxybenzo[d] thiazol-2-yl)hydrazine AldrichCPR](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/210/241/0c5be390-b73a-436d-82c7-c51156617e66/640/0c5be390-b73a-436d-82c7-c51156617e66.png)