S1073
Anti-STUB1/CHIP antibody, mouse monoclonal
clone ST21.55, purified from hybridoma cell culture
동의어(들):
Anti-C terminus of HSC70-interacting protein (CHIP), Anti-HSPABP2, Anti-Heat shock protein A binding protein 2 (c-terminal), Anti-NY-CO-7, Anti-SDCCAG7, Anti-STIP1 homologous and box-containing protein 1 (STUB1), Anti-Serologically defined colon cancer antigen 7, Anti-UBOX1
About This Item
추천 제품
생물학적 소스
mouse
결합
unconjugated
항체 형태
purified from hybridoma cell culture
항체 생산 유형
primary antibodies
클론
ST21.55, monoclonal
양식
buffered aqueous solution
분자량
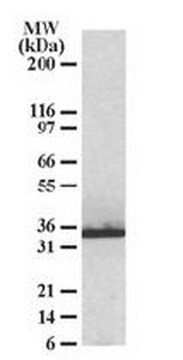
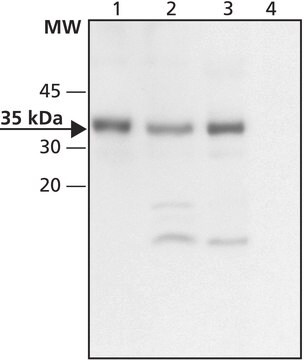
antigen ~35 kDa
종 반응성
rat, human, bovine
농도
~1.0 mg/mL
기술
indirect ELISA: suitable
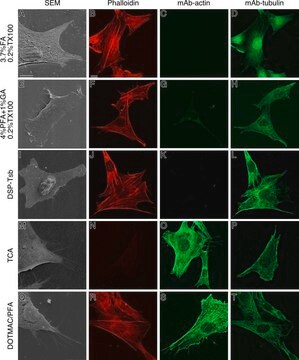
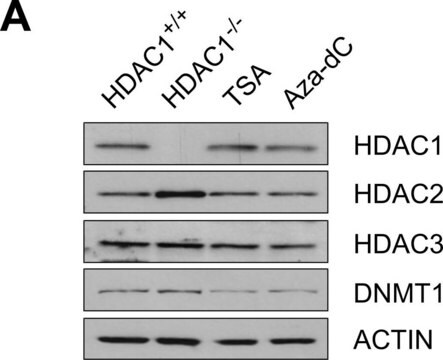
western blot: 2.5-5 μg/mL using HeLa total cell extract.
동형
IgG2b
UniProt 수납 번호
배송 상태
dry ice
저장 온도
−20°C
타겟 번역 후 변형
unmodified
유전자 정보
bovine ... STUB1(504565)
human ... STUB1(10273)
mouse ... Stub1(56424)
rat ... Stub1(287155)
일반 설명
면역원
애플리케이션
생화학적/생리학적 작용
물리적 형태
면책조항
적합한 제품을 찾을 수 없으신가요?
당사의 제품 선택기 도구.을(를) 시도해 보세요.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
개인 보호 장비
Eyeshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.