M3262
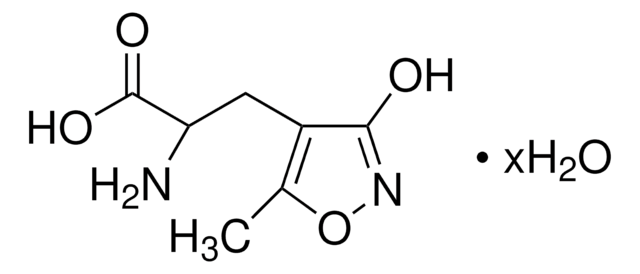
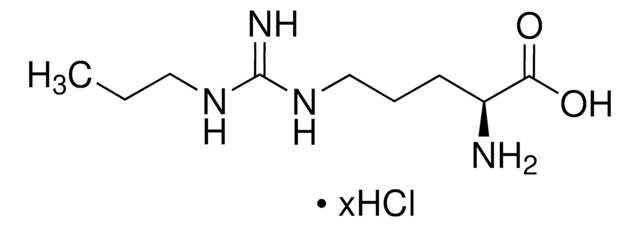
N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid
≥98% (TLC), suitable for cell culture
동의어(들):
(R)-2-(Methylamino)succinic acid, NMDA
About This Item
추천 제품
product name
N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid, ≥98% (TLC), solid
Quality Level
분석
≥98% (TLC)
형태
solid
기술
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
색상
white
mp
189-190 °C
응용 분야
cell analysis
SMILES string
CN[C@H](CC(O)=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C5H9NO4/c1-6-3(5(9)10)2-4(7)8/h3,6H,2H2,1H3,(H,7,8)(H,9,10)/t3-/m1/s1
InChI key
HOKKHZGPKSLGJE-GSVOUGTGSA-N
유전자 정보
human ... GRIN1(2902) , GRIN2A(2903) , GRIN2B(2904) , GRIN2C(2905) , GRIN2D(2906) , GRINA(2907)
rat ... Gria1(50592) , Grik1(29559) , Grin2a(24409)
유사한 제품을 찾으십니까? 방문 제품 비교 안내
일반 설명
애플리케이션
생화학적/생리학적 작용
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
개인 보호 장비
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
시험 성적서(COA)
제품의 로트/배치 번호를 입력하여 시험 성적서(COA)을 검색하십시오. 로트 및 배치 번호는 제품 라벨에 있는 ‘로트’ 또는 ‘배치’라는 용어 뒤에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
이미 열람한 고객
and tau proteolysis in rat cerebrocortical
neuronal cultures after ecstasy or
methamphetamine exposure.
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.