추천 제품
제품명
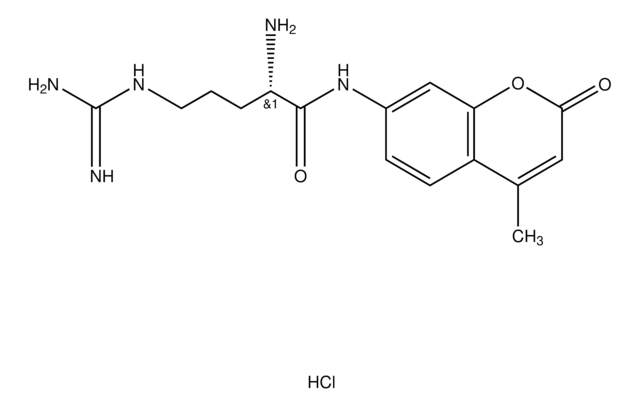
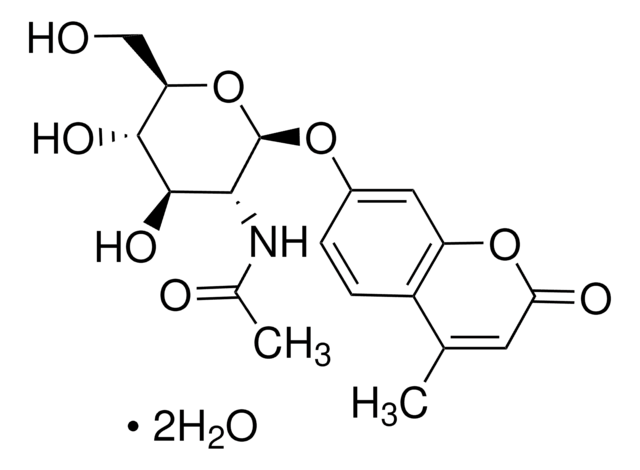
L-Leucine-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin hydrochloride,
분석
≥98% (TLC)
Quality Level
양식
powder
solubility
methanol: 50 mg/mL, clear, colorless to faintly yellow
형광
λex 327 nm; λem 349 nm (pH 8.0)
λex 380 nm; λem 440 nm (Reaction product)
저장 온도
−20°C
SMILES string
Cl.CC(C)C[C@H](N)C(=O)Nc1ccc2C(C)=CC(=O)Oc2c1
InChI
1S/C16H20N2O3.ClH/c1-9(2)6-13(17)16(20)18-11-4-5-12-10(3)7-15(19)21-14(12)8-11;/h4-5,7-9,13H,6,17H2,1-3H3,(H,18,20);1H/t13-;/m0./s1
InChI key
VCRXITKKWBOQRZ-ZOWNYOTGSA-N
일반 설명
L-Leucine-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin hydrochloride (Leu-AMC) is a fluorogenic peptidyl substrate for leucine aminopeptidase, an extracellular enzyme found abundantly in natural aquatic systems. This enzyme is one of the various enzymes used by bacteria for protein hydrolysis.
애플리케이션
L-Leucine-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin hydrochloride (Leu-AMC) as a substrate analog to determine leucine aminopeptidase activity
L-Leucine-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin hydrochloride has been used:
- as a substrate in fluorescence-based soil assays
- to determine leucine aminopeptidase activity of both Plasmodium falciparum M1 (PfA-M1) and PfA-M17 enzymes
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
개인 보호 장비
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
이미 열람한 고객
M17 leucine aminopeptidase of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium vivax
Lee JY, et al.
Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology, 170, 45-48 (2010)
Vincent Tardy et al.
Journal of hazardous materials, 411, 125121-125121 (2021-04-17)
Pharmaceutical industry effluents are complex and highly variable in time. Assessing the efficiency of a pharmaceutical industry wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) and the resulting decrease in effluent toxicity and ecological risk is thus not straightforward. We set up an original
Reconciling apparent variability in effects of biochar amendment on soil enzyme activities by assay optimization
Bailey VL, et al.
Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 43(2), 296-301 (2011)
Activity profiling of ectomycorrhiza communities in two forest soils using multiple enzymatic tests
Courty PE, et al.
The New phytologist, 167, 309-319 (2005)
Vincent Tardy et al.
Journal of hazardous materials, 411, 125121-125121 (2021-04-17)
Pharmaceutical industry effluents are complex and highly variable in time. Assessing the efficiency of a pharmaceutical industry wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) and the resulting decrease in effluent toxicity and ecological risk is thus not straightforward. We set up an original
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.