추천 제품
생물학적 소스
bovine brain (microvessels)
Quality Level
포장
pkg of 500,000 cells
제조업체/상표
Cell Applications, Inc
성장 모드
Adherent
핵형
2n = 60
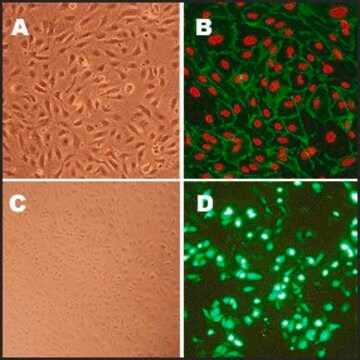
형태학
Endothelial
기술
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
관련 질환(들)
acquired immunodeficiency syndrome/human immunodeficiency virus (AIDS/HIV); ischemia/reperfusion injury
배송 상태
dry ice
저장 온도
−196°C
일반 설명
Lot specific orders are not able to be placed through the web. Contact your local sales rep for more details.
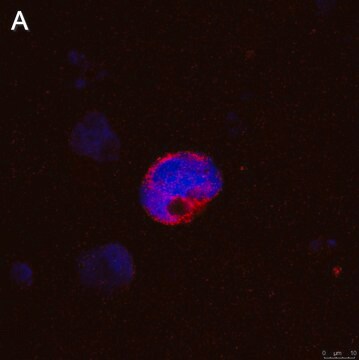
BBMVEC provide an excellent model system to study many aspects of endothelial function and disease, especially those related to the blood-brain barrier (BBB).
BBMVEC have been utilized extensively in research, for example to:
BBMVEC provide an excellent model system to study many aspects of endothelial function and disease, especially those related to the blood-brain barrier (BBB).
BBMVEC have been utilized extensively in research, for example to:
- Show, along with Bovine Aortic Endothelial Cells, that brain microvasculature is more sensitive to pathogenesis, compared to large vessel endothelia, by demonstrating that C-reactive protein (CRP), a cardiovascular risk factor, induces higher oxidative stress in the brain microvasculature due to higher local expression of the CRP-receptors CD16, CD32 and of the NAD(P)H-oxidase subunit p22phox (Closhen, 2010) and that brain microvascular endothelial cells show higher sensitivity to oxidative stress generated by advanced glycation end products due to stronger VEGF expression leading to increased permeability (Niiya, 2006, 2012); illustrating another difference between endothelia, alkalosis was shown to activate ERK in aortic, but not brain microvascular endothelial cells (Motz, 2006)
- Show that stronger blood-brain barrier (BBB) function can result from shear stress which acts through VE-cadherin mediated activation of Tiam/Rac1 pathway (Walsh, 2011) which in turn leads to upregulation of occludin and ZO-1 expression and increases their localization to tight junctions (Colgan, 2006, 2007) and by fluvastatin, which activates NO synthase and causes NO-dependent dephosphorylation of endothelial MLC via the MLC phosphatase (Kuhlmann, 2006), and is able to prevent glutamate-induced damage to the BBB (Kuhlmann, 2008); conversely, BBB breaks down under hypoxic conditions and as the result to CRP exposure due to MLCK and NADPH-oxidase activation, indicating that increased contractility and oxidative stress are involved in development of post-stroke brain edema (Kuhlmann, 2007, 2009)
- Support the key role of ROS by showing that activation of antioxidant genes by Nrf2 reduces brain vascular leak from acute high altitude exposure known to induce ROS (Lisk, 2013);
- Determine that IL-1β, ZYM, and LTA increase the permeability of the BBB to small ions, while TNF-α and lipopolysaccharide disrupt the endothelial layer integrity to allow passage of larger molecules (Pyrgos, 2010)
- Investigate the role of basolateral environment in modulating BBB by regulating expression and biochemical properties of the tight junction proteins, occludin and ZO-1 (Colgan, 2008)
- Show that during cerebral ischemia increased expression of TWEAK and Fn14 in the endothelial-astrocyte interface facilitating leukocyte transmigration and recruitment to the ischemic tissue (Haile, 2010)
- Study the mechanisms of BBB penetration by fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans during invasive cryptococcosis (Stie, 2012a, b)
- Demonstrate opposite effects of two osteoponin isoforms on the angiogenesis in the in vitro capillary assay and VEGF secretion by endothelial cells (Blasberg, 2010)
- Demonstrate that apigenin, a dietary flavonoid, activates Ca2+-activated K+ channels in endothelial cells leading to a hyperpolarization followed by a Ca2+ influx causing increased NO production followed by Akt dephosphorylation (Erdogan, 2007);
- Investigate the mechanisms of accumulation and effects of amyloid deposits on brain vasculature in cerebral amyloid angiopathy (Kandimalla, 2009; Agyare, 2013)
- Develop gene and drug delivery methods for crossing the BBB based on polymer-based nanoparticles (Agyare, 2008; Gil, 2009, 2012) or adenovirus or gold nanoparticles modified to be transported via transcytosis pathway (Tang, 2006; Prades, 2012), as well as to improve the general drug loading/delivery stealth dendrimer carriers (Yang, 2008)
세포주 기원
Microvessels
애플리케이션
endothelial function, growth factor expression, cell permeability, tight junction study, endothelial layer integrity, leukocyte transmigration, angiogenesis, in vitro capillary assay, growth factor secretion, K+ channel study, drug development
성분
Bovine Brain Endothelial Cell Basal Medium containing 10% FBS & 10% DMSO
제조 메모
- 2nd passage, >500,000 cells in Bovine Brain Endothelial Cell Basal Medium containing 10% FBS & 10% DMSO
- Can be cultured at least 12 doublings
계대배양 정규 작업
Please refer to the BBMVEC Culture Protocol.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
시험 성적서(COA)
제품의 로트/배치 번호를 입력하여 시험 성적서(COA)을 검색하십시오. 로트 및 배치 번호는 제품 라벨에 있는 ‘로트’ 또는 ‘배치’라는 용어 뒤에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
문서
Technical information for working with bovine brain microvascular endothelial cells including thawing, subculturing and cryopreservation
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.