추천 제품
생물학적 소스
goat
Quality Level
결합
alkaline phosphatase conjugate
항체 형태
affinity isolated antibody
항체 생산 유형
secondary antibodies
클론
polyclonal
양식
buffered aqueous solution
종 반응성
mouse
기술
direct ELISA: 1:3,000 using IgG, IgA, IgM
western blot: 1:50 dilution
배송 상태
wet ice
저장 온도
2-8°C
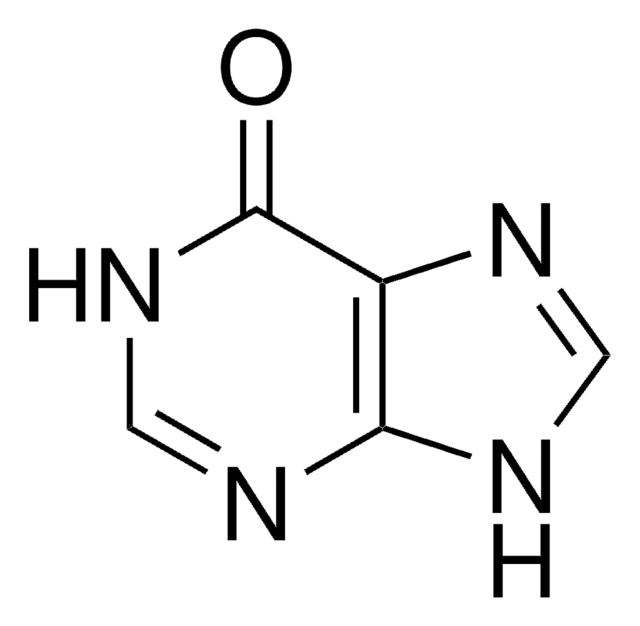
타겟 번역 후 변형
unmodified
관련 카테고리
일반 설명
Immunoglobulins are proteins produced by B cells in response to antigen and regulate response to bacteria and viruses. IgG is known to regulate complement fixation and placental transport. IgA has a crucial role in mucosal immunity as it restricts pathogens from entering the mucosal membrane. IgM is the largest antibody having a pentameric structure which modulates polyreactivity and removes apoptotic cells.
애플리케이션
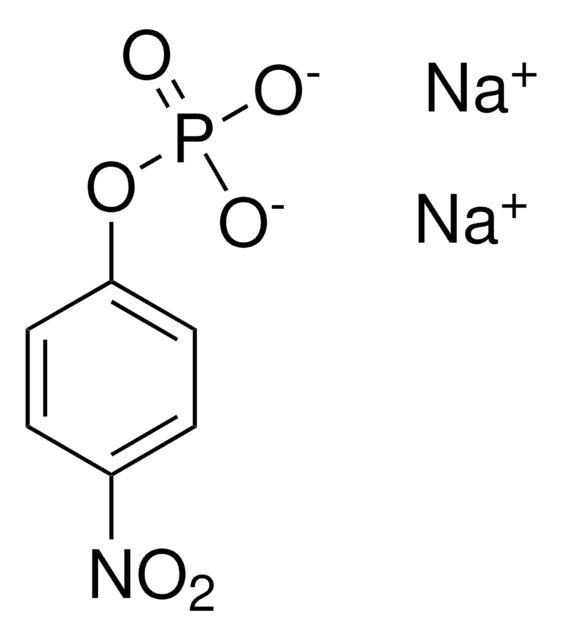
Alkaline-phosphatase-conjugated anti-mouse polyvalent immunoglobulin was used to detect antibodies from hybridomas by indirect ELISA. The antibody was incubated in microtiter plates for 1 hour at 37°C and detected using p-nitrophenyl phosphate substrate (Sigma). Alkaline-phosphatase-conjugated anti-mouse polyvalent immunoglobulin was used to detect the reactivity of fungal cytoplasmic protein with proteins from the serum of mice infected with yeast-form Y cells by western blot analysis. The antibody was used at a 1:50 dilution.
물리적 형태
Solution in 0.05 M Tris, pH 8.0, containing 1% bovine serum albumin, 1 mM MgCl2 and 15 mM sodium azide.
면책조항
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
적합한 제품을 찾을 수 없으신가요?
당사의 제품 선택기 도구.을(를) 시도해 보세요.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
이미 열람한 고객
Julien de Lorgeril et al.
Nature communications, 9(1), 4215-4215 (2018-10-13)
Infectious diseases are mostly explored using reductionist approaches despite repeated evidence showing them to be strongly influenced by numerous interacting host and environmental factors. Many diseases with a complex aetiology therefore remain misunderstood. By developing a holistic approach to tackle
C Tartera et al.
Applied and environmental microbiology, 56(5), 1397-1399 (1990-05-01)
Monoclonal antibodies provide a rapid and specific means of direct detection of microorganisms in water and food samples. However, monoclonal antibodies specific for some bacteria are difficult to obtain; a good example of such a bacterium is Escherichia coli. Gnotobiotic
Carla Bromuro et al.
Infection and immunity, 70(10), 5462-5470 (2002-09-14)
Mice immunized with heat-inactivated, whole yeast-form cells (Y cells) of Candida albicans developed intense, specific humoral and cell-mediated immune responses. However, they were modestly protected against a lethal challenge by the fungus, and their sera did not confer passive protection
Jonas Nilsson et al.
Glycoconjugate journal, 26(9), 1171-1180 (2009-04-24)
Noroviruses and norovirus virus-like particles (VLPs) exhibit strain specific patterns in their binding to ABH and Lewis histo-blood group antigens. In this study we demonstrate for the first time specific binding of Norwalk virus VLPs to type 1 and type
David A Six et al.
Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 58(1), 153-161 (2013-10-23)
The β-acetoacetyl-acyl carrier protein synthase FabY is a key enzyme in the initiation of fatty acid biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Deletion of fabY results in an increased susceptibility of P. aeruginosa in vitro to a number of antibiotics, including vancomycin
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.